Question 1:
You work as a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. What is the effect on the trust boundary of configuring the command mls qos trust cos on the switch port that is connected to the IP phone?
A – Effectively the trust boundary has been moved to the IP phone.
B – The host is now establishing the CoS value and has effectively become the trust boundary.
C – The switch SW is rewriting packets it receives from the IP phone and determining the CoS value.
D – The switch SW will no longer tag incoming voice packets and will trust the distribution layer switch to set the CoS.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The “mls qos trust cos” command is used to configure the port trust state (by default, the port is not trusted). By using this command, you can configure the switch port to which the telephone is connected to trust the CoS labels of all traffic received on that port.
(Note: All current Cisco IP Phones include an internal three-port Layer 2 switch therefore you can think an IP Phone as a switch and network administrators generally accept a Cisco IP Phone as a trusted device.)
Question 2:
If you are a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. Which switch interface configuration command would automatically configure quality of service (QoS) for voice over IP (VoIP) within a QoS domain?
A. auto qos voip cisco-phone
B. mls qos trust
C. switchport priority extend cos 7
D. switchport priority extend trust
Answer: A
Explanation:
The command “mls qos trust” is used to configure the port trust state (by default, the port is not trusted).
The command “switchport priority extend cos 7″ sets the IP phone port to override the priority received from the PC or the attached device (7 is the highest priority).
The command “switchport priority extend trust” tells the Cisco IP Phone to trust the CoS value of the connected PC without remark all packets sent form PC to CoS 0, by default.
Question 3:
Study the exhibit carefully. Which statement is true about the voice traffic coming to the switch access port that is connected to the IP phone?
A. The voice VLAN must be configured as a native VLAN on the switch.
B. A PC connected to a switch port via an IP phone must support a trunking encapsulation.
C. The traffic on the voice VLAN must be tagged with 802.1p encapsulation in order to coexist on the same LAN segment with a PC.
D. A PC connected to a switch port via an IP phone is unaware of the presence of the phone.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The voice VLAN can be configured over a unique voice VLAN (known as the voice VLAN ID or VVID) or over native VLAN -> A is not correct.
The ports k between PC and IP Phone are always functioned as access-mode switch ports so there is no need to support a trunking encapsulation -> B is not correct.
The traffic on the voice VLAN can be tagged with 802.1p encapsulation or 802.1q encapsulation -> C is not correct.
Most Cisco IP Phone models operate as a three-port switch as shown below. Nowadays, the voice traffic and data traffic will normally be on different IP subnets and the IP Phone is unaware of the presence of the phone.
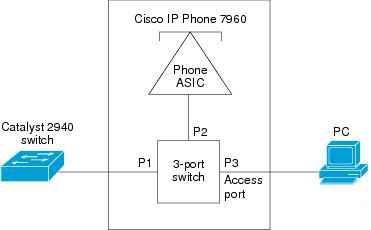
Question 4:
Study the exhibit carefully. Which statement is true when voice traffic is forwarded on the same VLAN used by the data traffic?
A. Quality of service cannot be applied for the voice traffic.
B. The voice traffic cannot be forwarded to the distribution layer.
C. Port security cannot be enabled on the switch that is attached to the IP phone.
D. The voice traffic cannot use 802.1p priority tagging.
Answer: D
Question 5:
Which two codes are supported by Cisco VoIP equipment?
A. G.701 and G719
B. G.711 and G.729
C. G.721 and G.739
D. G.731 and G.749
Answer: B
Question 6:
Study the exhibit carefully, then tell me what is the problem with this configuration?
 A – Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port where a voice VLAN is configured.
A – Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port where a voice VLAN is configured.
B – The switch port must be configured as a trunk.
C – Sticky secure MAC addresses cannot be used on a port when a voice VLAN is configured.
D – Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port when a sticky secure MAC address is used.
Answer: C
Question 7
What does the interface subcommand “switchport voice vlan 222″ indicate?
A. The port is configured for data and voice traffic.
B. The port is fully dedicated to forwarding voice traffic.
C. The port operates as an FXS telephony port.
D. Voice traffic is directed to VLAN 222.
Answer: A or D
Explanation
Let’s see an example of configuring this command.
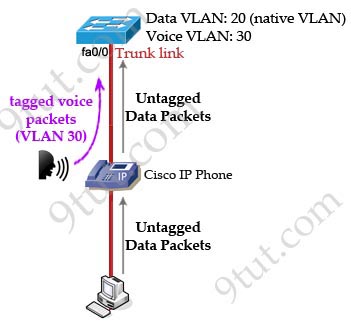
Switch(config)#interface fa0/0
Switch(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 30
The “switchport voice vlan 30″ command directs the switch to send CDP packets that configure the IP phone to transmit voice traffic in 802.1Q frames, tagged with VLAN 30. The data traffic is sent to the native VLAN (untagged).
Therefore in this question both answer A and D are correct. I don’t know why we only have one choice in this question.
Question 8
During the implementation of a voice solution, which two required items are configured at an access layer switch that will be connected to an IP phone to provide VoIP communication? (Choose two)
A. allowed codecs
B. untagged VLAN
C. auxiliary VLAN
D. Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP address
E. RSTP
Answer: B C
Explanation
An IP phone contains an integrated three-port 10/100 switch. The ports, which are dedicated connections, are described as follows:
* Port 1 connects to the Catalyst series switch or other device that supports Voice-over-IP (VoIP).
* Port 2 is an internal 10/100 interface that carries the phone traffic.
* Port 3 connects to a PC or other device.
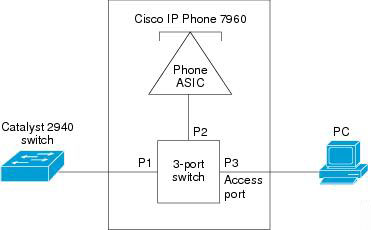 To enhance the quality of the VoIP traffic, port 2 and port 3 are often placed in two different VLANs. The VLAN carries voice traffic to and from the IP Phone is often called auxiliary VLAN (Port 2 in this case) while the VLAN carries data traffic is often the native VLAN (Port 3 in this case).
To enhance the quality of the VoIP traffic, port 2 and port 3 are often placed in two different VLANs. The VLAN carries voice traffic to and from the IP Phone is often called auxiliary VLAN (Port 2 in this case) while the VLAN carries data traffic is often the native VLAN (Port 3 in this case).
In the picture below the auxiliary VLAN is VLAN 30 while the native VLAN is VLAN 20. To use the IP Phone these two VLANs will need to be configured on the switch.

You work as a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. What is the effect on the trust boundary of configuring the command mls qos trust cos on the switch port that is connected to the IP phone?

B – The host is now establishing the CoS value and has effectively become the trust boundary.
C – The switch SW is rewriting packets it receives from the IP phone and determining the CoS value.
D – The switch SW will no longer tag incoming voice packets and will trust the distribution layer switch to set the CoS.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The “mls qos trust cos” command is used to configure the port trust state (by default, the port is not trusted). By using this command, you can configure the switch port to which the telephone is connected to trust the CoS labels of all traffic received on that port.
(Note: All current Cisco IP Phones include an internal three-port Layer 2 switch therefore you can think an IP Phone as a switch and network administrators generally accept a Cisco IP Phone as a trusted device.)
Question 2:
If you are a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. Which switch interface configuration command would automatically configure quality of service (QoS) for voice over IP (VoIP) within a QoS domain?
A. auto qos voip cisco-phone
B. mls qos trust
C. switchport priority extend cos 7
D. switchport priority extend trust
Answer: A
Explanation:
The command “mls qos trust” is used to configure the port trust state (by default, the port is not trusted).
The command “switchport priority extend cos 7″ sets the IP phone port to override the priority received from the PC or the attached device (7 is the highest priority).
The command “switchport priority extend trust” tells the Cisco IP Phone to trust the CoS value of the connected PC without remark all packets sent form PC to CoS 0, by default.
Question 3:
Study the exhibit carefully. Which statement is true about the voice traffic coming to the switch access port that is connected to the IP phone?
A. The voice VLAN must be configured as a native VLAN on the switch.
B. A PC connected to a switch port via an IP phone must support a trunking encapsulation.
C. The traffic on the voice VLAN must be tagged with 802.1p encapsulation in order to coexist on the same LAN segment with a PC.
D. A PC connected to a switch port via an IP phone is unaware of the presence of the phone.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The voice VLAN can be configured over a unique voice VLAN (known as the voice VLAN ID or VVID) or over native VLAN -> A is not correct.
The ports k between PC and IP Phone are always functioned as access-mode switch ports so there is no need to support a trunking encapsulation -> B is not correct.
The traffic on the voice VLAN can be tagged with 802.1p encapsulation or 802.1q encapsulation -> C is not correct.
Most Cisco IP Phone models operate as a three-port switch as shown below. Nowadays, the voice traffic and data traffic will normally be on different IP subnets and the IP Phone is unaware of the presence of the phone.

Question 4:
Study the exhibit carefully. Which statement is true when voice traffic is forwarded on the same VLAN used by the data traffic?
A. Quality of service cannot be applied for the voice traffic.
B. The voice traffic cannot be forwarded to the distribution layer.
C. Port security cannot be enabled on the switch that is attached to the IP phone.
D. The voice traffic cannot use 802.1p priority tagging.
Answer: D
Question 5:
Which two codes are supported by Cisco VoIP equipment?
A. G.701 and G719
B. G.711 and G.729
C. G.721 and G.739
D. G.731 and G.749
Answer: B
Question 6:
Study the exhibit carefully, then tell me what is the problem with this configuration?

B – The switch port must be configured as a trunk.
C – Sticky secure MAC addresses cannot be used on a port when a voice VLAN is configured.
D – Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port when a sticky secure MAC address is used.
Answer: C
Question 7
What does the interface subcommand “switchport voice vlan 222″ indicate?
A. The port is configured for data and voice traffic.
B. The port is fully dedicated to forwarding voice traffic.
C. The port operates as an FXS telephony port.
D. Voice traffic is directed to VLAN 222.
Answer: A or D
Explanation
Let’s see an example of configuring this command.

Switch(config)#interface fa0/0
Switch(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 30
The “switchport voice vlan 30″ command directs the switch to send CDP packets that configure the IP phone to transmit voice traffic in 802.1Q frames, tagged with VLAN 30. The data traffic is sent to the native VLAN (untagged).
Therefore in this question both answer A and D are correct. I don’t know why we only have one choice in this question.
Question 8
During the implementation of a voice solution, which two required items are configured at an access layer switch that will be connected to an IP phone to provide VoIP communication? (Choose two)
A. allowed codecs
B. untagged VLAN
C. auxiliary VLAN
D. Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP address
E. RSTP
Answer: B C
Explanation
An IP phone contains an integrated three-port 10/100 switch. The ports, which are dedicated connections, are described as follows:
* Port 1 connects to the Catalyst series switch or other device that supports Voice-over-IP (VoIP).
* Port 2 is an internal 10/100 interface that carries the phone traffic.
* Port 3 connects to a PC or other device.

In the picture below the auxiliary VLAN is VLAN 30 while the native VLAN is VLAN 20. To use the IP Phone these two VLANs will need to be configured on the switch.
