Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Which Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) statement is true about the roles of the master virtual router and the backup virtual router?
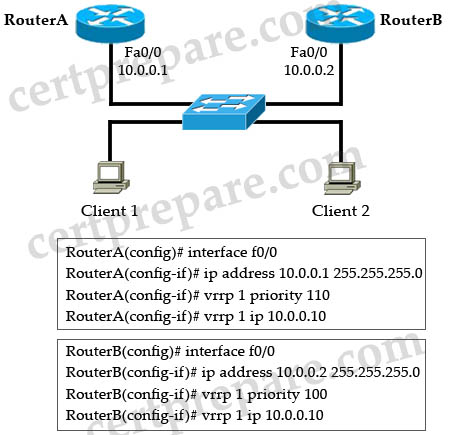 A. Router A is the master virtual router, and Router B is the backup virtual router. When Router A fails, Router B will become the master virtual router. When Router A recovers, Router B will maintain the role of master virtual router.
A. Router A is the master virtual router, and Router B is the backup virtual router. When Router A fails, Router B will become the master virtual router. When Router A recovers, Router B will maintain the role of master virtual router.
B. Router A is the master virtual router, and Router B is the backup virtual router. When Router A fails, Router B will become the master virtual router. When Router A recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
C. Router B is the master virtual router, and Router A is the backup virtual router. When Router B fails, Router A will become the master virtual router. When Router B recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
D. Router B is the master virtual router, and Router A is the backup virtual router. When Router B fails, Router A will become the master virtual router. When Router B recovers, Router A will maintain the role of master virtual router.
Answer: B
Explanation
RouterA is the master virtual router because of higher priority value.
By default, a preemptive scheme is enabled whereby a higher priority backup virtual router that becomes available takes over for the backup virtual router that was elected to become master virtual router. You can disable this preemptive scheme using the no vrrp preempt command. If preemption is disabled, the backup virtual router that is elected to become master virtual router remains the master until the original master virtual router recovers and becomes master again.
-> B is correct.
Question 2
Which one of the statements below correctly describes the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), which is being used in the Company network to provide redundancy?
A. A VRRP group has one active and one or more standby virtual routers.
B. A VRRP group has one master and one or more backup virtual routers.
C. A VRRP group has one master and one redundant virtual router.
D. A VRRP group has one active and one backup virtual router
Answer: B
Explanation
Unilike HSRP (which has one active router, one standby router and many listening routers), a VRRP group has one master router and one or more backup routers. All backup routers are in backup state.
Question 3
Which router redundancy protocol cannot be configured for interface tracking?
A. GLBP
B. HSRP
C. RPR
D. VRRP
E. SLB
F. RPR+
Answer: D
Explanation
VRRP cannot directly track an interface status but interfaces can be tracked through a tracked object. Notice that HSRP and GLBP can track both object and interface status.
Question 4
Which protocol will enable a group of routers to form a single virtual router and will use the real IP address of a router as the gateway address?
A. Proxy ARP
B. HSRP
C. IRDP
D. VRRP
E. GLBP
Answer: D
Explanation
VRRP is similar to HSRP but. However, with VRRP the IP address used can be either a virtual one or the actual IP address of the primary router.
Note: With HSRP, two or more devices support a virtual router with a fictitious MAC address and unique IP address. Hosts use
this IP address as their default gateway.
Question 5
If you are a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. Which Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) statement is true about the roles of the master virtual router and the backup virtual router?
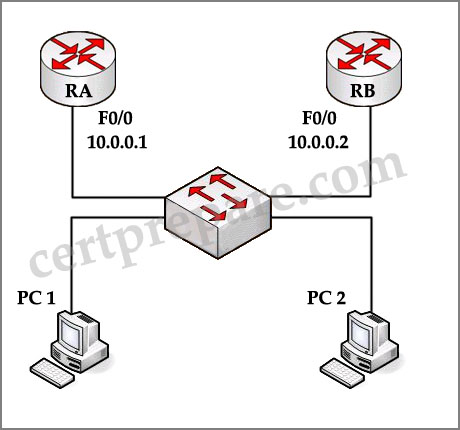
A – Router RA is the master virtual router, and Router RB is the backup virtual router. When Router RA fails, Router RB will become the master virtual router. When Router RA recovers, Router RB will maintain the role of master virtual router.
B – Router RA is the master virtual router, and Router RB is the backup virtual router. When Router RA fails, Router RB will become the master virtual router. When Router RA recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
C – Router RB is the master virtual router, and Router RA is the backup virtual router. When Router RB fails, Router RA will become the master virtual router. When Router RB recovers, RouterRA will maintain the role of master.
D – Router RB is the master virtual router, and Router RA is the backup virtual router. When Router RB fails, Router
RA will become the master virtual router. When Router RB recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Router RA is the master virtual router because of its higher priority (110). By default, the pre-empting function is enabled so Router RB will become the master virtual router when RA fails; and when RA recovers, it will take the master role again.
Refer to the exhibit. Which Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) statement is true about the roles of the master virtual router and the backup virtual router?

B. Router A is the master virtual router, and Router B is the backup virtual router. When Router A fails, Router B will become the master virtual router. When Router A recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
C. Router B is the master virtual router, and Router A is the backup virtual router. When Router B fails, Router A will become the master virtual router. When Router B recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
D. Router B is the master virtual router, and Router A is the backup virtual router. When Router B fails, Router A will become the master virtual router. When Router B recovers, Router A will maintain the role of master virtual router.
Answer: B
Explanation
RouterA is the master virtual router because of higher priority value.
By default, a preemptive scheme is enabled whereby a higher priority backup virtual router that becomes available takes over for the backup virtual router that was elected to become master virtual router. You can disable this preemptive scheme using the no vrrp preempt command. If preemption is disabled, the backup virtual router that is elected to become master virtual router remains the master until the original master virtual router recovers and becomes master again.
-> B is correct.
Question 2
Which one of the statements below correctly describes the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), which is being used in the Company network to provide redundancy?
A. A VRRP group has one active and one or more standby virtual routers.
B. A VRRP group has one master and one or more backup virtual routers.
C. A VRRP group has one master and one redundant virtual router.
D. A VRRP group has one active and one backup virtual router
Answer: B
Explanation
Unilike HSRP (which has one active router, one standby router and many listening routers), a VRRP group has one master router and one or more backup routers. All backup routers are in backup state.
Question 3
Which router redundancy protocol cannot be configured for interface tracking?
A. GLBP
B. HSRP
C. RPR
D. VRRP
E. SLB
F. RPR+
Answer: D
Explanation
VRRP cannot directly track an interface status but interfaces can be tracked through a tracked object. Notice that HSRP and GLBP can track both object and interface status.
Question 4
Which protocol will enable a group of routers to form a single virtual router and will use the real IP address of a router as the gateway address?
A. Proxy ARP
B. HSRP
C. IRDP
D. VRRP
E. GLBP
Answer: D
Explanation
VRRP is similar to HSRP but. However, with VRRP the IP address used can be either a virtual one or the actual IP address of the primary router.
Note: With HSRP, two or more devices support a virtual router with a fictitious MAC address and unique IP address. Hosts use
this IP address as their default gateway.
Question 5
If you are a network technician, study the exhibit carefully. Which Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) statement is true about the roles of the master virtual router and the backup virtual router?

| RA(config)# interface f0/0 RA(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 RA(config-if)# vrrp 1 priority 110 RA(config-if)# vrrp 1 ip 10.0.0.10 |
| ——————————————————————— RB(config)# interface f0/0 RB(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 RB(config-if)# vrrp 1 priority 100 RB(config-if)# vrrp 1 ip 10.0.0.10 |
B – Router RA is the master virtual router, and Router RB is the backup virtual router. When Router RA fails, Router RB will become the master virtual router. When Router RA recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
C – Router RB is the master virtual router, and Router RA is the backup virtual router. When Router RB fails, Router RA will become the master virtual router. When Router RB recovers, RouterRA will maintain the role of master.
D – Router RB is the master virtual router, and Router RA is the backup virtual router. When Router RB fails, Router
RA will become the master virtual router. When Router RB recovers, it will regain the master virtual router role.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Router RA is the master virtual router because of its higher priority (110). By default, the pre-empting function is enabled so Router RB will become the master virtual router when RA fails; and when RA recovers, it will take the master role again.