Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Which interoperability technique implemented on the dual-stack routers would allow connectivity between IPv6 sites across automatic created tunnels using the 2002::/16 prefix?
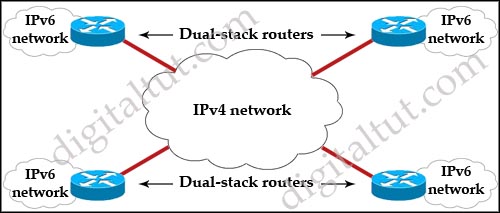
A. Dual Stack
B. NAT-PT
C. 6to4 tunnel
D. GRE tunnel
E. ISATAP tunnel
Answer: C
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 2
To configure 6to4 on a dual-stack edge router. Which three of the following are valid in 6to4 Tunneling configuration? (Choose three)
A. IPv4 Tunnel IP address
B. Tunnel mode (6to4)
C. Tunnel Keepalives
D. IPv4 Tunnel Destination
E. IPv4 Tunnel Source
F. 6to4 IPv6 address (within 2002::/16)
Answer: B E F
Question 3
Which three techniques can be used to transition from IPv4 to IPv6? (Select three)
A. Dual stack
B. NAT
C. Flow label
D. Mobile IP
E. 6to4 tunneling
F. Anycast
G. MBGP
Answer: A B E
Explanation
Dual stack is the most common technique which only requires edge routers to run both IPv4 and IPv6 while the inside routers only run IPv4. At the edge network, IPv4 packets are converted to IPv6 packets before sending out.
The Network Address Translator – Protocol Translator (NAT-PT) defines a set of network-layer translation mechanisms designed to allow nodes that only support IPv4 to communicate with nodes that only support IPv6, during the transition to the use of IPv6 in the Internet.
NAT-PT provides IPv4/IPv6 protocol translation. It resides within an IP router, situated at the boundary of an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network. By installing NAT-PT between an IPv4 and IPv6 network, all IPv4 users are given access to the IPv6 network without modification in the local IPv4-hosts (and vice versa). Equally, all hosts on the IPv6 network are given access to the IPv4 hosts without modification to the local IPv6-hosts. This is accomplished with a pool of IPv4 addresses for assignment to IPv6 nodes on a dynamic basis as sessions are initiated across IPv4-IPv6 boundaries
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 4
Which two statements about 6to4 tunneling are accurate? (Choose two)
A. Prepending a reserved IPv6 code to the hexadecimal representation of 192.168.0.1 facilitates 6to4 tunneling
B. Each 6to4 site receives a /48 prefix in a 6to4 tunnel
C. 2002::/48 is the address range specifically assigned to 6to4
D. Prepending 0×2002 with the IPv4 address creates an IPv6 address that is used in 6to4 tunneling
E. 6to4 is a manual tunnel method
Answer: B D
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
Because the border-router-IPv4-address is added, we will have a /48 prefix (we all know an IPv4 address consists of 32 bits). An example of a 6to4 address with the border-router-IPv4-address of 192.168.1.2 is 2002:C0A8:01:02::/48.
Question 5
Which two statements are true about 6to4 tunnels? (Choose two)
A. In a 6to4 tunnel, the first two bytes of the IPv6 address will be 0×2002 and the next four bytes will be the hexadecimal equivalent of the IPv4 address.
B. In a 6to4 tunnel, the first two bytes of the IPv6 address will be locally derived and the next two bytes will be the hexadecimal equivalent of the IPv4 address.
C. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:c0a8:6301::/48 IPv6 address.
D. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:c0a8:6301::/16 IPv6 address.
E. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:1316:4463:1::/64 IPv6 address.
Answer: A C
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 6
When implementing a 6to4 tunnel, which IPv6 address is the correct translation of the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1?
A. c0a8:6301:2002::/48
B. 2002:c0a8:6301::/48
C. 2002:c0a8:6301::/8
D. 2002::/16
Answer: B
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. If R1 is configured for 6to4 tunneling, what will the prefix of its IPv6 network be?

A. 1723:1100:1::/48
B. FFFF:AC1F:6401::/16
C. AC1F:6401::/32
D. 2002:AC1F:6401::/48
E. 3FFE:AC1F:6401::/32
Answer: D
Refer to the exhibit. Which interoperability technique implemented on the dual-stack routers would allow connectivity between IPv6 sites across automatic created tunnels using the 2002::/16 prefix?

B. NAT-PT
C. 6to4 tunnel
D. GRE tunnel
E. ISATAP tunnel
Answer: C
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 2
To configure 6to4 on a dual-stack edge router. Which three of the following are valid in 6to4 Tunneling configuration? (Choose three)
A. IPv4 Tunnel IP address
B. Tunnel mode (6to4)
C. Tunnel Keepalives
D. IPv4 Tunnel Destination
E. IPv4 Tunnel Source
F. 6to4 IPv6 address (within 2002::/16)
Answer: B E F
Question 3
Which three techniques can be used to transition from IPv4 to IPv6? (Select three)
A. Dual stack
B. NAT
C. Flow label
D. Mobile IP
E. 6to4 tunneling
F. Anycast
G. MBGP
Answer: A B E
Explanation
Dual stack is the most common technique which only requires edge routers to run both IPv4 and IPv6 while the inside routers only run IPv4. At the edge network, IPv4 packets are converted to IPv6 packets before sending out.
The Network Address Translator – Protocol Translator (NAT-PT) defines a set of network-layer translation mechanisms designed to allow nodes that only support IPv4 to communicate with nodes that only support IPv6, during the transition to the use of IPv6 in the Internet.
NAT-PT provides IPv4/IPv6 protocol translation. It resides within an IP router, situated at the boundary of an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network. By installing NAT-PT between an IPv4 and IPv6 network, all IPv4 users are given access to the IPv6 network without modification in the local IPv4-hosts (and vice versa). Equally, all hosts on the IPv6 network are given access to the IPv4 hosts without modification to the local IPv6-hosts. This is accomplished with a pool of IPv4 addresses for assignment to IPv6 nodes on a dynamic basis as sessions are initiated across IPv4-IPv6 boundaries
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 4
Which two statements about 6to4 tunneling are accurate? (Choose two)
A. Prepending a reserved IPv6 code to the hexadecimal representation of 192.168.0.1 facilitates 6to4 tunneling
B. Each 6to4 site receives a /48 prefix in a 6to4 tunnel
C. 2002::/48 is the address range specifically assigned to 6to4
D. Prepending 0×2002 with the IPv4 address creates an IPv6 address that is used in 6to4 tunneling
E. 6to4 is a manual tunnel method
Answer: B D
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
Because the border-router-IPv4-address is added, we will have a /48 prefix (we all know an IPv4 address consists of 32 bits). An example of a 6to4 address with the border-router-IPv4-address of 192.168.1.2 is 2002:C0A8:01:02::/48.
Question 5
Which two statements are true about 6to4 tunnels? (Choose two)
A. In a 6to4 tunnel, the first two bytes of the IPv6 address will be 0×2002 and the next four bytes will be the hexadecimal equivalent of the IPv4 address.
B. In a 6to4 tunnel, the first two bytes of the IPv6 address will be locally derived and the next two bytes will be the hexadecimal equivalent of the IPv4 address.
C. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:c0a8:6301::/48 IPv6 address.
D. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:c0a8:6301::/16 IPv6 address.
E. In a 6to4 tunnel, the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1 would be converted to the 2002:1316:4463:1::/64 IPv6 address.
Answer: A C
Explanation
6to4 tunnel is a technique which relies on reserved address space 2002::/16 (you must remember this range). These tunnels determine the appropriate destination address by combining the IPv6 prefix with the globally unique destination 6to4 border
router’s IPv4 address, beginning with the 2002::/16 prefix, in this format:
2002:border-router-IPv4-address::/48
For example, if the border-router-IPv4-address is 64.101.64.1, the tunnel interface will have an IPv6 prefix of 2002:4065:4001:1::/64, where 4065:4001 is the hexadecimal equivalent of 64.101.64.1.
Question 6
When implementing a 6to4 tunnel, which IPv6 address is the correct translation of the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1?
A. c0a8:6301:2002::/48
B. 2002:c0a8:6301::/48
C. 2002:c0a8:6301::/8
D. 2002::/16
Answer: B
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. If R1 is configured for 6to4 tunneling, what will the prefix of its IPv6 network be?

A. 1723:1100:1::/48
B. FFFF:AC1F:6401::/16
C. AC1F:6401::/32
D. 2002:AC1F:6401::/48
E. 3FFE:AC1F:6401::/32
Answer: D