Question 1
Which three statements about the EIGRP routing protocol are true? (Choose three)
A – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.9
B – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.10
C – EIGRP supports five generic packet types. including hello, update, query, reply, and ACK packets
D – EIGRP supports five generic packet types, including hello, database description (DBD), link-state request (LSR), link-state update (LSU), and LSAck
E – E. EIGRP will form a neighbor relationship with another peer even when their K values are mismatched
F – A. EIGRP will not form a neighbor relationship with another peer when their K values are mismatched
Answer: B, C, F
Question 2
After DUAL calculations, a router has identified a successor route, but no routes have qualified as a feasible successor. In the event that the current successor goes down, what process will EIGRP use in the selection of a new successor?
A – EIGRP will find the interface with the lowest MAC address
B – The route will transition to the active state
C – The route will transition to the passive state
D – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest feasible distance (FD)
E – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest advertised distance (AD)
Answer: B
Explanation
When a route (current successor) goes down, the router first checks its topology table for a feasible successor but it can’t find one. So it goes active on the that route to find a new successor by sending queries out to its neighbors requesting a path to the lost route.
Question 3
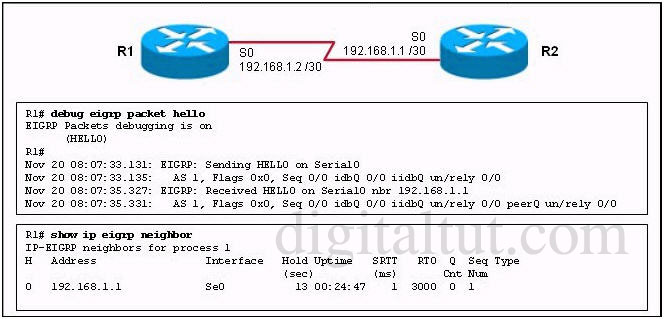
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 have established a neighbor relationship and are exchanging routing information. The network design requires that R1 receive routing updates from R2, but not advertise any routes to R2. Which configuration command sequence will successfully accomplish this task?
A – R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
B – R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
C – R1(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
D – R2(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
E – R1(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
F – R2(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
Answer: C
Explanation
We can not use passive-interface to accomplish this task because the “passive-interface…” command (in EIGRP or OSPF) will shut down the neighbor relationship of these two routers (no hello packets are exchanged). And to filter routing updates we should configure a distribute list on R1 with an access list that deny all and apply it to the outbound direction so that R1 can receive but can not send routing updates.
Question 4
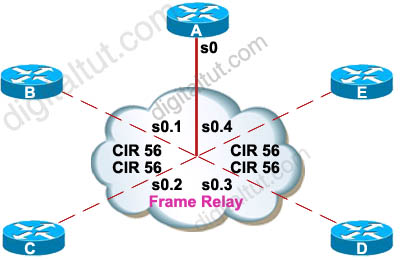
EIGRP has been configured to operate over Frame Relay multipoint connections. What should the bandwidth command be set to?
A – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection multiplied by the number of circuits
B – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection
C – the CIR rate of the highest speed connection
D – the sum of all the CIRs divided by the number of connections
Answer: A
Explanation
If the multipoint network has different speeds allocated to the VCs, take the lowest CIR and simply multiply it by the number of circuits. This is because in Frame-relay all neighbors share the bandwidth equally, regardless of the actual CIR of each individual PVC, so we have to get the lowest speed CIR rate and multiply it by the number of circuits. This result will be applied on the main interface (or multipoint connection interface).
Question 5
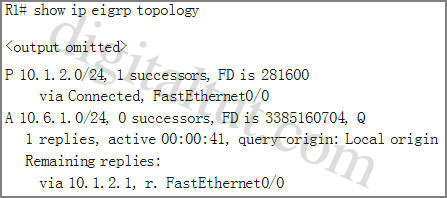
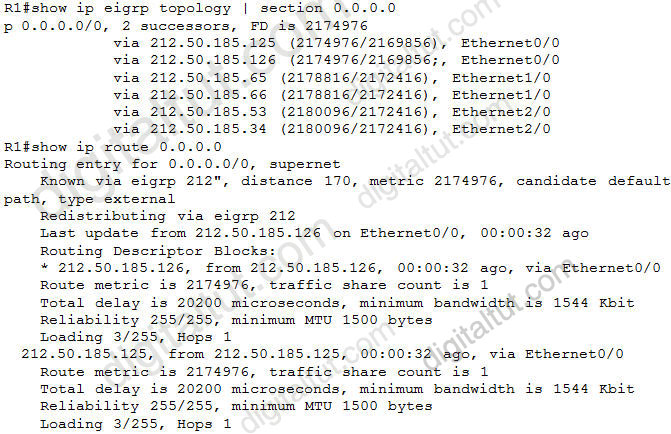
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured on all routers in the network. On a basis of the show ip eigrp topology output provided, what conclusion can be derived?
A – Router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 out of interface FastEthernet0/0
B – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out before it declares the neighbor unreachable
C – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out inquiring for a second successor to network 10.6.1.0/24
D – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 in response to the query sent out about network 10.6.1.0/24
Answer: D
Explanation
From the output, we notice that there is an active route (A) and the reply status flag (r) was set. An active EIGRP route is the state when a network change occurs and a feasible successor is not found by a EIGRP router for a given route (10.6.1.0/24); and the reply status flag (r) means that R1′s queries were sent out to the neighbors asking for routing information to the 10.6.1.0/24 network but hasn’t received a reply yet. Therefore the answer A – router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 is not correct because router R1 can’t find a path to that network. Answers B and C are not correct because R1 doesn’t send a hello message but a query asking for routing information to the desired network.
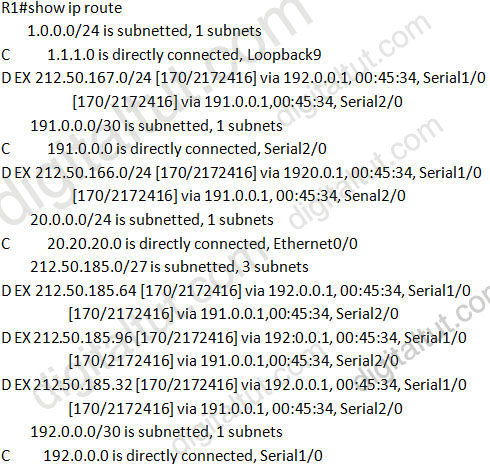
Question 6
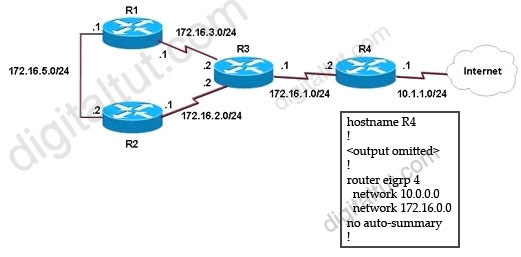
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on all routers in the network. What additional configuration statement should be included on router R4 to advertise a default route to its neighbors?
 A. R4(config)#ip default-network 10.0.0.0
A. R4(config)#ip default-network 10.0.0.0
B. R4(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
C. R4(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
D. R4(config-router)# default-information originate
Answer: A
Explanation
The “ip default-network ” command will direct other routers to send its unknown traffic to this network. Other router (R1,R2,R3) will indicate this network as the “Gateway of last resort”.
There is another way to route unknown traffic to 10.1.1.0/24 network: create a static route using “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2″ command then inject this route using the “network 0.0.0.0″ command, or using “redistribute static” command.
Note: In EIGRP, default routes cannot be directly injected (as they can in OSPF with the default-information originate command. Also, EIGRP does not have the “default-information originate” command).
Question 7
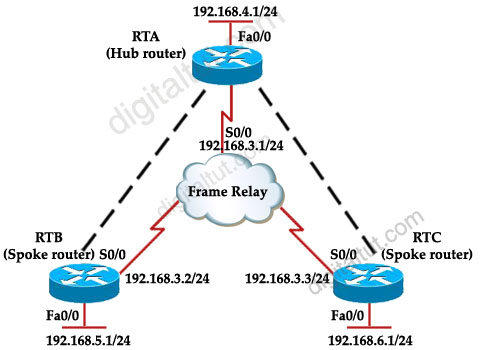
Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC are not receiving each other’s routes. What is the solution?
 A. Configure the auto summary command under router eigrp 1 on router RTA.
A. Configure the auto summary command under router eigrp 1 on router RTA.
B. Issue the no ip split horizon command on router RTA.
C. Configure subinterfaces on the spoke routers and assign different IP address subnets for each subinterface.
D. Check and change the access lists on router RTA.
E. Issue the no ip split horizon eigrp 1 command on router RTA.
Answer: E
Explanation
RTB and RTC cannot see each other because of the split horizon rule: “A router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. To overcome this problem we can configure subinterfaces or disable split horizon with the command “no ip split horizon eigrp 1″ on RTA.
Question 8
When troubleshooting an EIGRP connectivity problem, you notice that two connected EIGRP routers are not becoming EIGRP neighbors. A ping between the two routers was successful. What is the next thing that should be checked?
A. Verify that the EIGRP hello and hold timers match exactly.
B. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP peer command.
C. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP traffic command.
D. Verify that EIGRP is enabled for the appropriate networks on the local and neighboring router.
Answer: D
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. You are the network administrator of the Route.com company. You have been tasked to implement a hub and spoke EIGRP topology over Frame Relay to provide connectivity between the networks at headquarters and all 300 spokes.
Before you begin the actual implementation, which three pieces of information are more important to know than the others? (Choose three)
 A. the Committed Information Rate of all the Frame Relay PVCs
A. the Committed Information Rate of all the Frame Relay PVCs
B. the Cisco IOS version running on all the routers
C. the router model number of all the spoke routers
D. the number of HQ networks connected behind the headquarter routers
E. the routing policy, such as whether or not the spokes can be used as backup transient point between the two headquarter routers
Answer: A B E
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. The Route.com company is running EIGRP between all the routers. Currently, if one of the LAN links (LAN1 or LAN2) at the headquarters flaps (goes up and down), the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers will experience high CPU usage and have a long EIGRP convergence time. As the new network administrator, you are asked to investigate this situation and determine if there is a quick way to resolve this issue.
Which is the most important thing that you can quickly verify first to resolve this issue?
 A. Verify that the bandwidth setting on all WAN links is correct.
A. Verify that the bandwidth setting on all WAN links is correct.
B. Verify that the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers are configured to send only a default route to all the spoke routers.
C. Verify that the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers are configured for EIGRP Nonstop Forwarding.
D. Verify that all the spoke routers are configured for autosummarization.
E. Verify that all the spoke routers are configured as EIGRP stub.
Answer: E
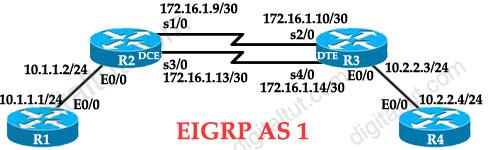
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. When you examine the routing table of R1 and R4, you are not able to see the R1 Ethernet subnet on the R4 routing table. You are also not able to see the R4 Ethernet subnet on the R1 routing table.
Which configuration change should be made to resolve this issue? Select the routers where the configuration change will be required, and select the required EIGRP configuration command(s). (Choose two)
 A. R1 and R4
A. R1 and R4
B. R2 and R3
C. ip summary-address eigrp 1 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 and ip summary-address eigrp 1
D. variance 2
E. eigrp stub connected
F. no auto-summary
Answer: B F
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit. The actual speed of the serial links between R2 and R3 are 256 kb/s and 512 kb/s respectively. When configuring EIGRP on routers R2 and R3, the network administrator configured the bandwidth of both serial interfaces to 512 kb/s. What will be the effect?
 A. EIGRP will overutilize the 512 kb/s link.
A. EIGRP will overutilize the 512 kb/s link.
B. The interface “delay” value used in the EIGRP metric calculation will be inaccurate on the 256 kb/s serial interface.
C. The amount of bandwidth used for EIGRP routing protocol traffic on the 256 kb/s link can become excessive.
D. EIGRP can load balance between the two serial links only if the variance is set to 2 or higher.
E. Unequal cost load balancing will be disabled.
Answer: C
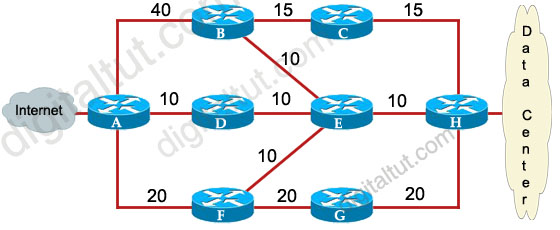
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com has just implemented this EIGRP network. A network administrator came to you for advice while trying to implement load balancing across part of their EIGRP network.
If the variance value is configured as 2 on all routers and all other metric and K values are configured to their default values, traffic from the Internet to the data center will be load balanced across how many paths?
 A. 1
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: C
Explanation
First we should list all the paths from the Internet to the data center:
+ A-B-C-H with a metric of 70 (40 + 15 + 15)
+ A-B-E-H with a metric of 60 (40+10+10)
+ A-D-E-H with a metric of 30 (10+10+10)
+ A-D-E-B-C-H with a metric of 60 (10+10+10+15+15)
+ A-D-E-F-G-H with a metric of 70 (10+10+10+20+20)
+ A-F-G-H with a metric of 60 (20+20+20)
+ A-F-E-H with a metric of 40 (20+10+10)
So the path A-D-E-H will be chosen because it has the best metric. But EIGRP can support unequal cost path load balancing. By configuring the variance value of 2, the minimum metric is increased to 60 (30 * 2) and all the routes that have a metric of less than or equal to 60 and satisfy the feasibility condition will be used to send traffic.
Besides the main path A-D-E-H we have 4 more paths that have the metric of less than or equal to 60 (we also include the Advertised Distances of these routes for later comparison):
+ A-B-E-H with an AD of 20
+ A-D-E-B-C-H with an AD of 50
+ A-F-G-H with an AD of 40
+ A-F-E-H with an AD of 20
Now the last thing we need to consider is the feasible condition. The feasible condition states:
“To qualify as a feasible successor, a router must have an AD less than the FD of the current successor route”
The FD of the current successor route here is 30 (notice that the variance number is not calculated here). Therefore there are only 2 paths that can satisfy this conditions: the path A-B-E-H & A-F-E-H.
In conclusion, traffic from the Internet to the data center will be load balanced across 3 paths, including the main path (successor path) -> C is correct.
Question 14
Which condition must be satisfied before an EIGRP neighbor can be considered a feasible successor?
A. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be less than or equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
B. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be less than the feasible distance of the current successor.
C. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be greater than the feasible distance of the current successor.
D. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
E. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be greater than or equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
Answer: B
Explanation
As explained in question 1, this is called the feasible condition.
Question 15
Which statement about a non-zero value for the load metric (k2) for EIGRP is true?
A. A change in the load on an interface will cause EIGRP to recalculate the routing metrics and send a corresponding update out to each of its neighbors.
B. EIGRP calculates interface load as a 5-minute exponentially weighted average that is updated every 5 minutes.
C. EIGRP considers the load of an interface only when sending an update for some other reason.
D. A change in the load on an interface will cause EIGRP to recalculate and update the administrative distance for all routes learned on that interface.
Answer: C
Explanation
The load metric (k2) represents the worst load on a link between source and destination.
EIGRP routing updates are triggered only by a change in network topology (like links, interfaces go up/down, router added/removed), and not by change in interface load or reliability -> A & D are not correct.
The load is a five minute exponentially weighted average that is updated every five seconds (not five minutes) -> B is not correct.
EIGRP considers the load of an interface only when sending an update for some other reason (like a link failure, topology change). Updates are not sent out each time the load changes -> C is correct.
Note: To learn how to calculate EIGRP metric, please read my EIGRP tutorial – Part 3.
Question 16
Your network consists of a large hub-and-spoke Frame Relay network with a CIR of 56 kb/s for each spoke.
Which statement about the selection of a dynamic protocol is true?
A. EIGRP would be appropriate if LMI type ANSI is NOT used.
B. EIGRP would be appropriate, because the Frame Relay spokes could be segmented into their own areas.
C. EIGRP would be appropriate, because by default, queries are not propagated across the slow speed Frame Relay links.
D. EIGRP would be appropriate, because you can manage how much bandwidth is consumed over the Frame Relay interface.
Answer: D
Explanation
By default, EIGRP will limit itself to using no more than 50% of the interface bandwidth. The primary benefit of controlling EIGRP’s bandwidth usage is to avoid losing EIGRP packets, which could occur when EIGRP generates data faster than the interface line can absorb it. This is of particular benefit on Frame Relay networks, where the access interface bandwidth and the PVC capacity may be very different.
For example, in our Frame Relay topology a Hub is connected with 4 Spoke routers. The main Frame Relay interface on Hub router is 512Kpbs which is not enough to use for 6 links of 128 Kbps ( = 768 Kbps).
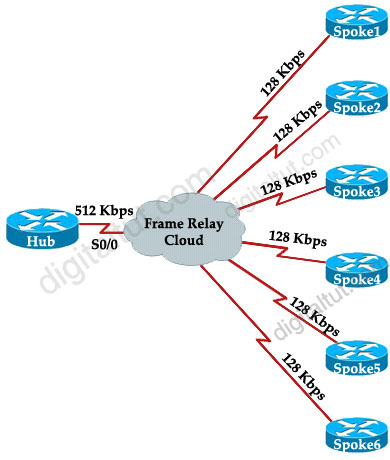 The solution here is we can use 512 / 6 = 85 Kbps on each subinterface of Hub by using “bandwidth 85″ command. For example:
The solution here is we can use 512 / 6 = 85 Kbps on each subinterface of Hub by using “bandwidth 85″ command. For example:
Hub(config)#interface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point
Hub(config-subif)#bandwidth 85
Also on Spoke routers we need to set this value. For example on Spoke1:
Spoke1(config)#interface Serial0/1.0 point-to-point
Spoke1(config-subif)#bandwidth 85
Notice that by default, EIGRP limits itself to use no more than 50% of the configured interface bandwidth. In this case EIGRP will not use more than 42.5 Kbps (50% of 85 Kbps).
Question 17
When an EIGRP topology change is detected, what is the correct order of events when there is a FS?
A.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
The feasible route is used.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
B.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used.
C.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
D.
DUAL is notified.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
The feasible route is used.
Answer: D
Question 18
Refer to the exhibit. You want to use all the routes in the EIGRP topology for IP load balancing.
Which two EIGRP subcommands would you use to accomplish this goal? (Choose two)
A. traffic-share balanced
B. distance
C. maximum-paths
D. default-network
E. variance
Answer: C E
Explanation
Notice that the “maximum-paths” command is used to share traffic to equal cost path while the “variance” command can share traffic to unequal cost path.
In the output above we learn that EIGRP is using 2 successors to send traffic. By using the “variance 2″ command we can share traffic to other feasible successor routes. But by default, EIGRP only shares traffic to 4 paths. So we need to use the “maximum-paths 6″ to make sure all of these routes are used.
Question 19
Refer to the exhibit. R1 accesses the Internet using E0/0. You have been asked to configure R1 so that a default route is generated to its downstream devices (191.0.0.1 and 192.0.0.1). Which commands would create this configuration?
A.
router eigrp 190
redistribute static
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0
B. ip default-network 20.0.0.0
C.
router eigrp 190
redistribute static
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 Null0
D. ip default-network 20.20.20.0
Answer: A
Question 20
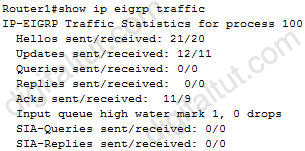
Which command will display EIGRP packets sent and received, as well as statistics on hello packets, updates, queries, replies, and acknowledgments?
A. debug eigrp packets
B. show ip eigrp traffic
C. debug ip eigrp
D. show ip eigrp interfaces
Answer: B
Explanation
Below is the output of the “show ip eigrp traffic” command:
Question 21
Which three statements are true about EIGRP operation? (Choose three)
A. When summarization is configured, the router will also create a route to null 0.
B. The summary route remains in the route table, even if there are no more specific routes to the network.
C. Summarization is configured on a per-interface level.
D. The maximum metric for the specific routes is used as the metric for the summary route.
E. Automatic summarization across major network boundaries is enabled by default.
Answer: A C E
Question 22
Which two statements about the EIGRP DUAL process are correct? (Choose two)
A. An EIGRP route will go active if there are no successors or feasible successors in the EIGRP topology table.
B. An EIGRP route will go passive if there are no successors in the EIGRP topology table.
C. DUAL will trigger an EIGRP query process while placing the flapping routes in the holddown state.
D. A feasible successor in the EIGRP topology table can become the successor only after all the query requests have been replied to.
E. The stuck in active state is caused when the wait for the query replies have timed out.
F. EIGRP queries are sent during the loading state in the EIGRP neighbor establishment process.
Answer: A E
Question 23
What are three key concepts that apply when configuring the EIGRP stub routing feature in a hub and spoke network? (Choose three)
A. A hub router prevents routes from being advertised to the remote router.
B. Only remote routers are configured as stubs.
C. Stub routers are not queried for routes.
D. Spoke routers connected to hub routers answer the route queries for the stub router.
E. A stub router should have only EIGRP hub routers as neighbors.
F. EIGRP stub routing should be used on hub routers only.
Answer: B C E
Question 24
Which three statements are true about EIGRP route summarization? (Choose three)
A. Manual route summarization is configured in router configuration mode when the router is configured for EIGRP routing.
B. Manual route summarization is configured on the interface.
C. When manual summarization is configured, the summary route will use the metric of the largest specific metric of the summary routes.
D. The ip summary-address eigrp command generates a default route with an administrative distance of 90.
E. The ip summary-address eigrp command generates a default route with an administrative distance of 5.
F. When manual summarization is configured, the router immediately creates a route that points to null0 interface
Answer: B E F
Explanation
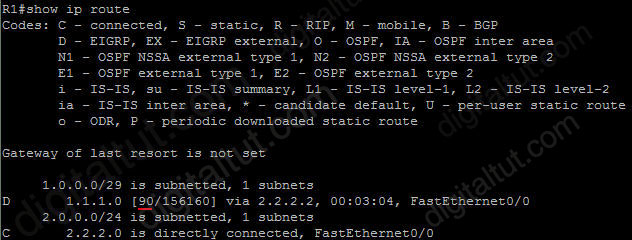
The ip summary-address eigrp {AS number} {address mask} command is used to configure a summary aggregate address for a specified interface. For example with the topology below:
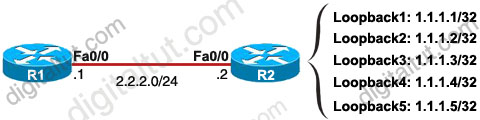 R2 has 5 loopback interfaces but instead of advertising all these interfaces we can only advertise its summarized subnet. In this case the best summarized subnet should be 1.1.1.0/29 which includes all these 5 loopback interfaces.
R2 has 5 loopback interfaces but instead of advertising all these interfaces we can only advertise its summarized subnet. In this case the best summarized subnet should be 1.1.1.0/29 which includes all these 5 loopback interfaces.
R2(config)#interface fa0/0
R2(config-if)#ip summary-address eigrp 1 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.248
This configuration causes EIGRP to summarize network 1.1.1.0 and sends out Fa0/0 interface
After configuring manual EIGRP summary, the routing table of the local router will have a route to Null0:
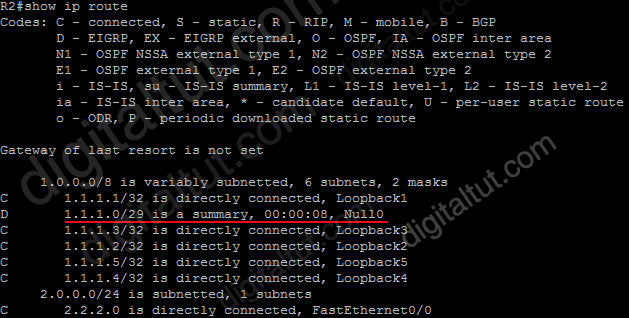
So why is this route inserted in the routing table when doing summarization? Well, you may notice that although our summarized subnet is 1.1.1.0/29 but we don’t have all IP addresses in this subnet. Assignable IP addresses of subnet 1.1.1.0/29 are from 1.1.1.1 to 1.1.1.6. Imagine what happens if R1 sends a packet to 1.1.1.6. Because R1 do believe R2 is connected with this IP so it will send this packet to R2. But R2 does not have this IP so if R2 has a default-route to R1 (for example R1 is connected to the Internet and R2 routes all unknown destination IP packets to R1) then a loop will occur.
To solve this problem, some routing protocols automatically add a route to Null0. A packet is sent to “Null0″ means that packet is dropped. Suppose that R1 sends a packet to 1.1.1.6 through R2, even R2 does not have a specific route for that IP, it does have a general route pointing to Null0 which the packet sent to 1.1.1.6 can be matched -> That packet is dropped at R2 without causing a routing loop!
By default, EIGRP summary routes are given an administrative distance value of 5. Notice that this value is only shown on the local router doing the summarization. On other routers we can still see an administrative distance of 90 in their routing table.
Question 25
After implementing EIGRP on your network, you issue the show ip eigrp traffic command on router C. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IF-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 481/444
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Approximately 25 minutes later, you issue the same command again. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 1057/1020
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Approximately 25 minutes later, you issue the same command a third time. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 1754/1717
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
What can you conclude about this network?
A. The network has been stable for at least the last 45 minutes.
B. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C knows an alternate path to the network.
C. There is a flapping link or interface, and router A does not know an alternate path to the network.
D. EIGRP is not working correctly on router C.
E. There is not enough information to make a determination.
Answer: A
Explanation
In three times using the command, the “Queries sent/received” & “Replies sent/received” are still the same -> the network is stable.
Question 26
After implementing EIGRP on your network, you issue the show ip eigrp traffic command on router C. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2112/2076
Updates sent/received: 47/38
Queries sent/received: 5/3
Replies sent/received: 3/4
Acks sent/received: 29/33
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Moments later, you issue the same command a second time and the following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2139/2104
Updates sent/received: 50/39
Queries sent/received: 5/4
Replies sent/received: 4/4
Acks sent/received: 31/37
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Moments later, you issue the same command a third time and the following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2162/2126
Updates sent/received: 53/42
Queries sent/received: 5/5
Replies sent/received: 5/4
Acks sent/received: 35/41
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
What information can you determine about this network?
A. The network is stable.
B. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C knows an alternate path to the network.
C. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C does not know an alternate path to the network.
D. EIGRP is not working correctly on router C.
E. There is not enough information to make a determination.
Answer: B
Explanation
We notice that the “Queries received” number is increased so router C has been asked for a route. The “Replies sent” number is also increased -> router C knows an alternate path to the network.
Question 27
R1 and R2 are connected and are running EIGRP on all their interfaces, R1 has four interfaces, with IP address 172.16.1.1/24, 172.16.2.3/24,172.16.5.1/24, and 10.1.1.1/24. R2 has two interfaces, with IP address 172.16.1.2/24 and 192.168.1.1/24. There are other routers in the network that are connected on each of the interfaces of these two routers that are also running EIGRP. Which summary routes does R1 generate automatically (assuming auto-summarization is enable)? (choose two)
A. 192.168.1.0/24
B. 10.0.0.0/8
C. 172.16.1.0/22
D. 172.16.0.0/16
E. 10.1.1.0/24
Answer: B D
Question 28
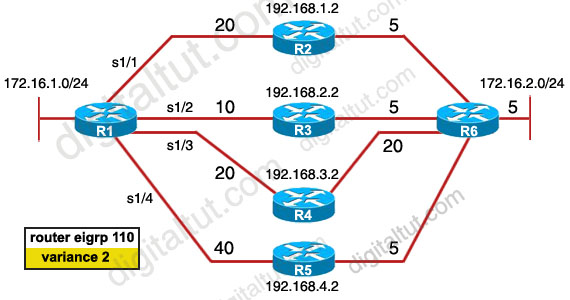 There was an exhibit, 172.16.1.0/24 to 172.16.2.0/24 with the 4 paths with mentions of eigrp metric and asked if the variance is put to 2 in exhibit then what 2 paths are not used by eigrp routing table? (Choose two)
There was an exhibit, 172.16.1.0/24 to 172.16.2.0/24 with the 4 paths with mentions of eigrp metric and asked if the variance is put to 2 in exhibit then what 2 paths are not used by eigrp routing table? (Choose two)
A. R1—R2—R6
B. R1—R3—R6
C. R1—R4—R6
D. R1—R5—R6
Answer: C D
Question 29
What does the default value of the EIGRP variance command of 1 mean?
A. Load balancing is disabled on this router.
B. The router performs equal-cost load balancing.
C. Only the path that is the feasible successor should be used.
D. The router only performs equal-cost load balancing on all paths that have a metric greater than 1.
Answer: B
Question 30
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on all routers in the network. The command metric weights 0 0 1 0 0 has been added to the EIGRP process so that only the delay metric is used in the path calculations. Which router will R1 select as the successor and feasible successor for Network A?
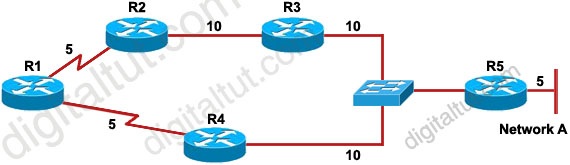 A. R4 becomes the successor for Network A and will be placed in the routing table. R2 becomes the feasible successor for Network A.
A. R4 becomes the successor for Network A and will be placed in the routing table. R2 becomes the feasible successor for Network A.
B. R4 becomes the successor for Network A and will be included in the routing table. No feasible successor will be selected as the advertised distance from R2 is higher than the feasible distance.
C. R2 becomes the successor and will be placed in the routing table. R4 becomes the feasible successor for Network A.
D. R2 becomes the successor and will be placed in the routing table. No feasible successor will be selected as the reported distance from R4 is lower than the feasible distance.
Answer: B
Question 31
Based on the exhibited output, which three statements are true? (Choose three)

A. R1 is in AS 200.
B. R1 will load balance between three paths to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix because all three paths have the same advertised distance (AD) of 40512000.
C. The best path for R1 to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix is via 192.168.1.66.
D. 40512000 is the advertised distance (AD) via 192.168.1.66 to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix.
E. All the routes are in the passive mode because these routes are in the hold-down state.
F. All the routes are in the passive mode because R1 is in the query process for those routes.
Answer: A C D
Explanation
In the statement “IP-EIGRP Topology Table for process 200″, process 200 here means AS 200 -> A is correct.
There are 3 paths to reach network 192.168.1.48/28 but there is only 1 path in the routing table (because there is only 1 successor) so the path with least FD will be chosen -> path via 192.168.1.66 with a FD of 40537600 will be chosen -> C is correct.
The other parameter, 40512000, is the AD of that route -> D is correct.
Question 32
Characteristics of the routing protocol EIGRP? (choose two)
A. Updates are sent as broadcast.
B. Updates are sent as multicast.
C. LSAs are sent to adjacent neighbors.
D. Metric values are represented in a 32-bit format for granularity.
Answer: B D
Explanation
EIGRP updates are sent as multicast to address 224.0.0.10 -> B is correct.
EIGRP metric values, for example an entry in the “show ip route” command:
D 10.1.21.128/27 [90/156160] via 10.1.4.5, 00:00:21, FastEthernet1/0/1
EIGRP metric here is 156160 and it is a 32-bit value.
Question 33
Which EIGRP packet statement is true?
A. On high-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 5 seconds for neighbor discovery.
B. On low-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 15 seconds for neighbor discovery.
C. Reply packets are multicast to IP address 224.0.0.10 using RTP.
D. Update packets route reliable change information only to the affected routers.
E. Reply packets are used to send routing updates.
Answer: D
Question 34
Which three descriptions are correct based on the exhibited output? (Choose three)
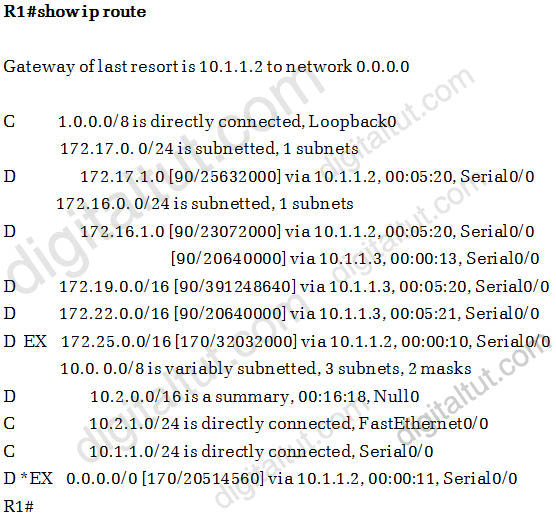 A. R1 is configured with the variance command.
A. R1 is configured with the variance command.
B. The route to 10.2.0.0/16 was redistributed into EIGRP.
C. A default route has been redistributed into the EIGRP autonomous system.
D. R1 is configured with the ip summary-address command.
Answer: A C D
Explanation
From the routing table above, we see that network 172.16.1. can be reached via 2 unequal paths (with FD of 23072000 & 20640000) so surely R1 has been configured with the “variance” command -> A is correct.
By configuring a default route and redistribute it into EIGRP you will get the line “D *EX 0.0.0.0/0 …” line in the routing table of that router -> C is correct.
From the line “10.2.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:16:18, Null0″ we know that this network has been summarized with the “ip summaray-address” command (notice that 10.2.0.0 is not the major network of net-> D is correct.
Question 35
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
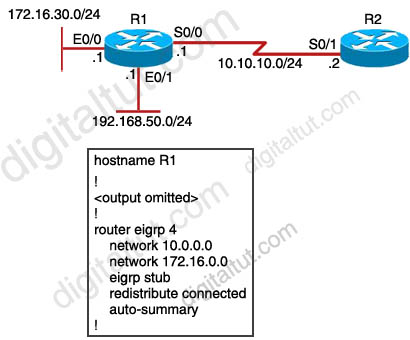 A. The eigrp stub command prevents queries from being sent from R2 to R1.
A. The eigrp stub command prevents queries from being sent from R2 to R1.
B. The eigrp stub command will automatically enable summarization of routes on R2.
C. The eigrp stub command prevents all routes except a default route from being advertised to R1.
D. Router R1 will advertise connected and summary routes only.
E. Router R1 will advertise connected and static routes. The sending of summary routes will not be permitted.
F. Router R1 is configured as a receive-only neighbor and will not send any connected, static or summary routes.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The command “eigrp stub” turns R1 into a stub router so R2 will never send any query to R1 because R2 knows that a stub router will only route packets for networks it has explicitly advertised -> A is correct.
The command “eigrp stub” is same as “eigrp stub connected summary” command because connected and summarized routes are advertised by default -> D is correct.
Note: Because the network 192.168.50.0 is not advertised by “network” statement, it is necessary to redistribute connected route with the “redistribute connected” command.
Question 36
Refer to the exhibits. Router B should advertise the network connected to the E0/0/0 interface to router A and block all other network advertisements. The IP routing table on router A indicates that it is not receiving this prefix from router B.
What is the probable cause of the problem?
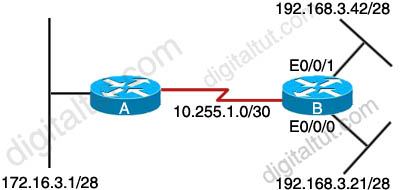
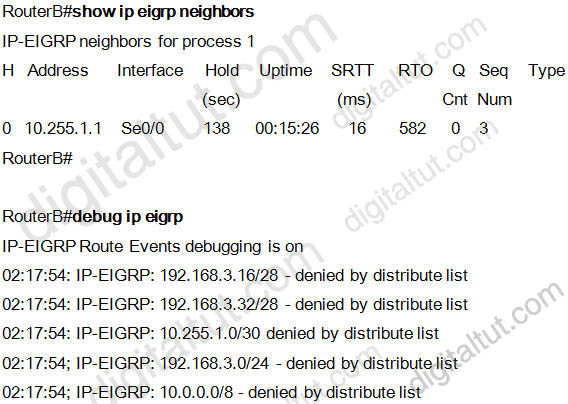 A. An access list on router B is causing the 192.168.3.16/28 network to be denied.
A. An access list on router B is causing the 192.168.3.16/28 network to be denied.
B. An access list on router B is causing the 192.168.3.32/28 network to be denied.
C. The distribute list on router B is referencing a numbered access list that does not exist on router B.
D. The distribute list on router B is referencing the wrong interface.
Answer: A
Explanation
This is an unclear question. The question says “Router B should advertise the network connected to the E0/0/0 interface to router A and block all other network advertisements. The IP routing table on router A indicates that it is not receiving this prefix from router B.” That means the network 192.168.3.16/28 (including the IP 192.168.3.21/28) is not received on router A -> A is the most suitable answer.
Note: Distribute list are used to filter routing updates and they are based on access lists.
Question 37
Study the exhibit carefully. What must be done on router A in order to make EIGRP work effectively in a Frame Relay multipoint environment?
 A. Issue the command bandwidth 56 on the physical interface.
A. Issue the command bandwidth 56 on the physical interface.
B. Issue the command bandwidth 56 on each subinterface.
C. Issue the command bandwidth 224 on each subinterface.
D. Issue the command bandwidth 224 on the physical interface.
Answer: D
Explanation
In Frame Relay, all neighbors share the same bandwidth, regardless of the actual CIR of each individual PVC. In this case the CIR of each PVC is the same so we can find the bandwidth of the main interface (multipoint connection interface) by 56 x 4 = 224.
Notice that if the bandwidth on each PVC is not equal then we get the lowest bandwidth to multiply.
Question 38
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE Enterprises has many stub networks in their enterprise network, such as router B and its associated network. EIGRP is to be implemented on router A so that neither the prefix for the S/0/0/0 interface nor the prefixes from router B appear in the routing tables for the router in the enterprise network.
Which action will accomplish this goal?
 A. Declare router B a stub router using the eigrp stub command.
A. Declare router B a stub router using the eigrp stub command.
B. Use the passive-interface command for interface Serial0/0/0.
C. Use a mask with the network command to exclude interface Serial0/0/0.
D. Implement a distribute list to exclude the link prefix from the routing updates.
Answer: C
Explanation
If we declare router B a stub router then the routers in Enterprise Network still learn about the network for S0/0/0 interface and the network behind router B -> A is not correct.
If we use the passive-interface command on s0/0/0 interface then router A & B can not become neighbor because they don’t exchange hello messages -> A can not send traffic to the network behind B -> B is not correct.
Theoretically, we can use a distribute list to exclude both the link prefix and the prefix from router B but it is not efficient because:
+ We have many stub networks so we will need a “long” distribute list.
+ We declare networks in stub routers (like router B) while filter them out at router A -> it is a waste.
I am not totally sure about answer C because if we “use a mask with the network command to exclude interface Serial0/0/0″ then router A and B can not become neighbors and the situation is same as answer B. But from many discussions about this question, maybe C is the best answer.
Question 39
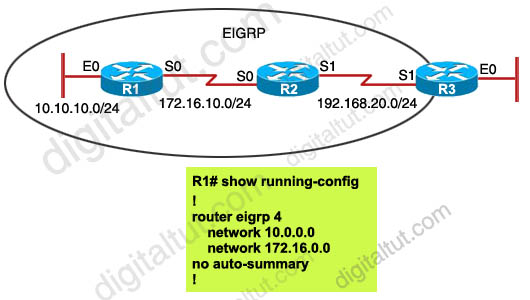
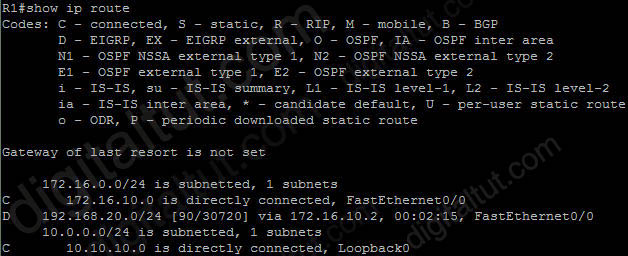
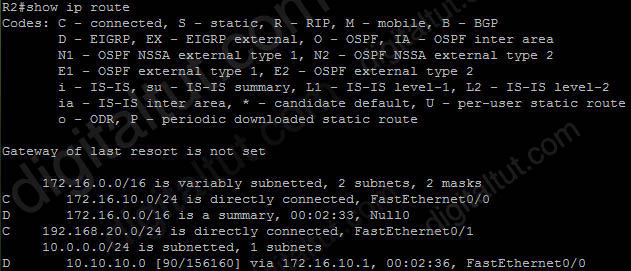
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured with the default configuration on all routers. Autosummarization is enabled on routers R2 and R3, but it is disabled on router R1. Which two EIGRP routes will be seen in the routing table of router R3? (Choose two)
 A. 10.0.0.0/8
A. 10.0.0.0/8
B. 10.10.0.0/16
C. 10.10.10.0/24
D. 172.16.0.0/16
E. 172.16.0.0/24
F. 172.16.10.0/24
Answer: C D
Explanation
EIGRP performs an auto-summarization each time it crosses a border between two different major networks. In this case all different networks are in different major networks so EIGRP will perform auto-summarization when it exits an interface. But R1 has been configured with “no auto-summary” command so EIGRP will not summarize on S0 interface of R1. So the routing table of R2 will have the network 10.10.10.0/24 (not be summarized).
When exiting S1 interface of R2, EIGRP summarizes network 172.16.10.0/24 into the major 172.16.0.0/16 network but it does not summarize network 10.10.10.0/24 because it is not directly connected with this network. Therefore in the routing table of R3 there will have:
+ Network 10.10.10.0/24 ( not summarized)
+ Network 172.16.0.0/16 (summarized)
-> C and D are correct.
Note: I simulated this question on GNS3, you can see the final outputs of the “show ip route” commands on these routers (I connected these routers via FastEthernet, not Serial interfaces so the outputs are slightly different but the main points are not changed).
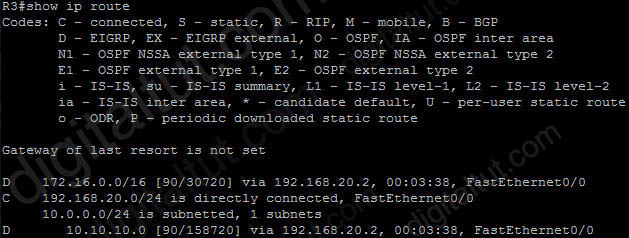
Question 40
Refer to the exhibit. In a redundant hub-and-spoke deployment using EIGRP, what feature can be used to ensure that routers C through F are not used as transit routers for data traveling from router B to network 10.1.1.0?
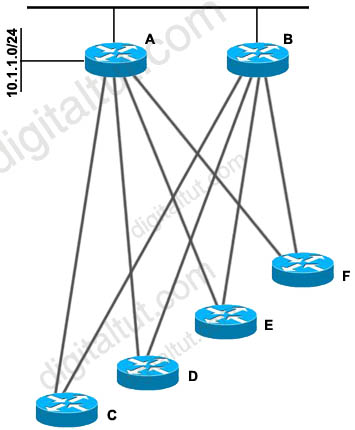 A. Use address summarization at routers C, D. E, and F.
A. Use address summarization at routers C, D. E, and F.
B. Use the EIGRP Stub feature on routers C, D, E, and F.
C. Use passive-interface on the spoke links in routers A and B.
D. Change the administrative distance in routers A and B for routes learned from routers Cr D. E, and F.
Answer: B
Explanation
By configuring “stub” feature on routers C D E and F, routers A and B will not try to transit traffic through these routers. For example, if the network connecting from routers A and B is down, router B will not send to network 10.1.1.0/24 from router B -> routerC/D/E/F -> router A -> network 10.1.1.0/24.
Question 41
Refer to the exhibit. How would you confirm on R1 that load balancing is actually occurring on the default-network (0.0.0.0)?
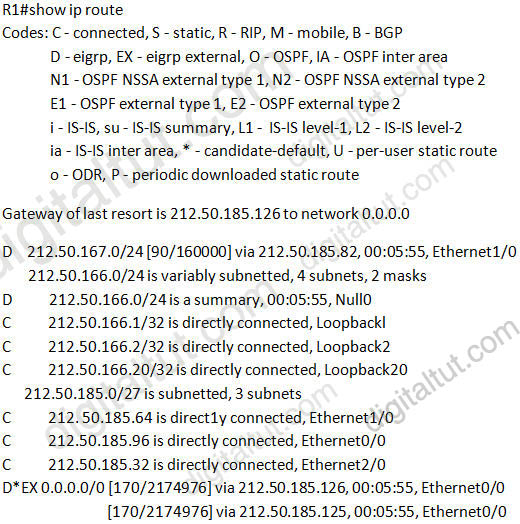
A. Use ping and the show ip route command to confirm the timers for each default network resets to 0.
B. Load balancing does not occur over default networks; the second route will only be used for failover.
C. Use an extended ping along with repeated show ip route commands to confirm the gateway of last resort address toggles back and forth.
D. Use the traceroute command to an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Answer: D
Explanation
The most simple method to test load balancing is to use the “traceroute” command. If load balancing is working correctly, we will see different paths to reach the destination each time we use that command.
Unknown address will be routed via the default-network 0.0.0.0 so we must use an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Question 42
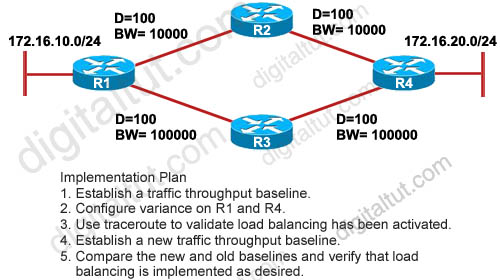
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com is planning to implement load balancing for traffic between host on the 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20./24 networks. You have been asked to review the implementation plan for this project. Which statement about the plan is true?
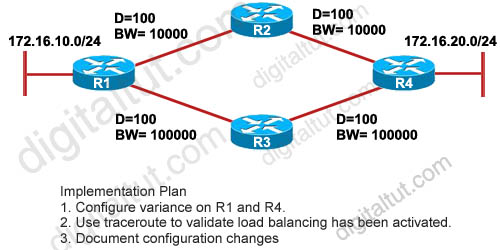 A. It is complete as written.
A. It is complete as written.
B. It should include a task to configure EIGRP multipath equal to 2 on R1 and R4.
C. It should include a task to implement OSPF because it handles unequal cost load balancing most efficiently using variance.
D. It should include a task that establishes a baseline before and after the configuration has been changed.
Answer: D
Explanation
A complete implementation plan should be:
1. Configure variance on R1 and R4
2. Use traceroute to validate load balancing has been activated
3. Document configuration changes
4. Establish a new traffic throughput baseline
5. Compare the new and old baselines and verify that load balancing is implemented as desired.
Question 43
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com is planning to implement load balancing for traffic between host on the 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20./24 networks. You have been asked to review the implementation plan for this project. Which statement about the plan is true?
 A. It is complete as written.
A. It is complete as written.
B. It should include a task to configure multipath to equal a value of 2 on R1 and R4.
C. It should use a ping instead of a traceroute to validate that load balancing has been activated.
D. It should contain a task that documents the changes made to the configurations.
Answer: D
Question 44
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP had converged in AS 1 when the link between router R1 and R2 went down. The console on router R2 generated the following messages:
The network administrator issued the show ip eigrp topology active command on R2 to check the status of the EIGRP network. Which statement best describes the reason for the error messages?
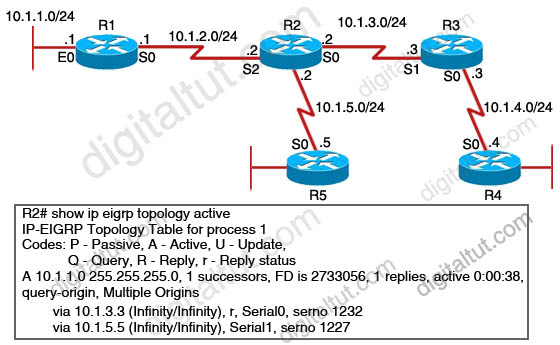 A. Incorrect bandwidth configuration on router R3 prevents R2 from establishing neighbor adjacency.
A. Incorrect bandwidth configuration on router R3 prevents R2 from establishing neighbor adjacency.
B. Incorrect bandwidth configuration on router R5 prevents R2 from establishing neighbor adjacency.
C. Router R3 did not reply to the query about network 10.1.1.0/24 sent by router R2.
D. Router R5 did not reply to the query about network 10.1.1.0/24 sent by router R2.
Answer: C
Explanation
When the link between R1 and R2 is down, R2 loses its successor for the network 10.1.1.0/24. R2 checks its topology table for a feasible successor but it can’t find one. So R2 goes active on the that route to find a new successor by sending queries out to its neighbors (R3 and R5) requesting a path to the lost route. Both R3 and R5 also go “active” for the that route. But R5 doesn’t have any neighbor to ask besides R2 so it will send an “unreachable message” to indicate it has no alternative path for that route and has no other neighbor to query. R3 also checks its EIRGP topology table for a feasible successor but it has none, too. Unlike R5, R3 has a neighbor (R4) so it continues to query this router.
Now suppose there is a problem on the link between R3 and R4 so R4 never receives the query from R3 and of course, R3 also never receives a reply back from R4. Therefore, R3 can’t reply back to R2. After about 3 minutes, the “Stuck in active” (SIA) timer on R2 expires and R2 marks the route 10.1.1.0/24 as “stuck in active” route.
The output line “via 10.1.3.3 (Infinity/Infinity), r, Seiral0, serno 1232″ indicates R2 has sent a query to 10.1.3.3 and is waiting for a reply (the lowercase r) -> C is correct.
Question 45
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on routers R1 and R2. However, R1 does not show R2 as a neighbor and does not accept routing updates from R2. What could be the cause of the problem?
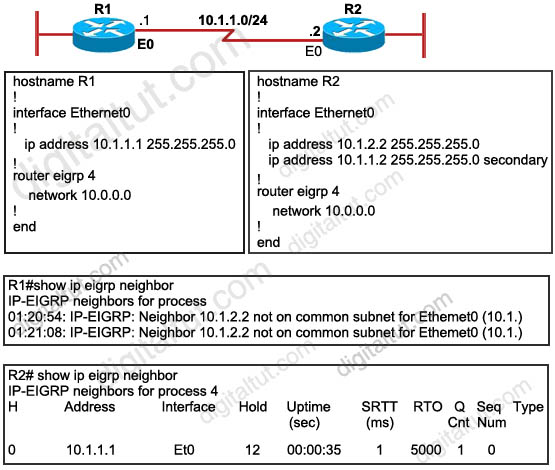 A. The no auto-summary command has not been issued under the EIGRP process on both routers.
A. The no auto-summary command has not been issued under the EIGRP process on both routers.
B. Interface E0 on router R1 has not been configured with a secondary IP address of 10.1.2.1/24.
C. EIGRP cannot exchange routing updates with a neighbor’s router interface that is configured with two IP addresses.
D. EIGRP cannot form neighbor relationship and exchange routing updates with a secondary address.
Answer: D
Explanation
EIGRP updates always use the primary IP address of the outgoing interface as the source address. In this case R2 will use the 10.1.2.2/24 address, which is not in the same subnet of R1, to send EIGRP update to R1. Therefore R1 does not accept this update and generates the “not on common subnet” error message.
Answer D is a bit unclear. It should state that “EIGRP cannot form neighbor relationship and exchange routing updates if the two primary addresses on two routers are not in the same subnet”.
Notice that although R1 does not accept R2 as its EIGRP neighbors but R2 accepts R1 as its EIGRP neighbor accepts R1 hello packets..
Question 46
Refer to the exhibit. A Boston company bought the assets of a New York company and is trying to route traffic between the two data networks using EIGRP over EoMPLS. As a network consultant, you were asked to verify the interoperability of the two networks.
From the show ip route command output, what can you tell the customer about the traffic flow between the subnet in New York (172.16.8.0/24) and the subnets in Boston (172.16.16.0/24 and 10.10.16.0/24)?
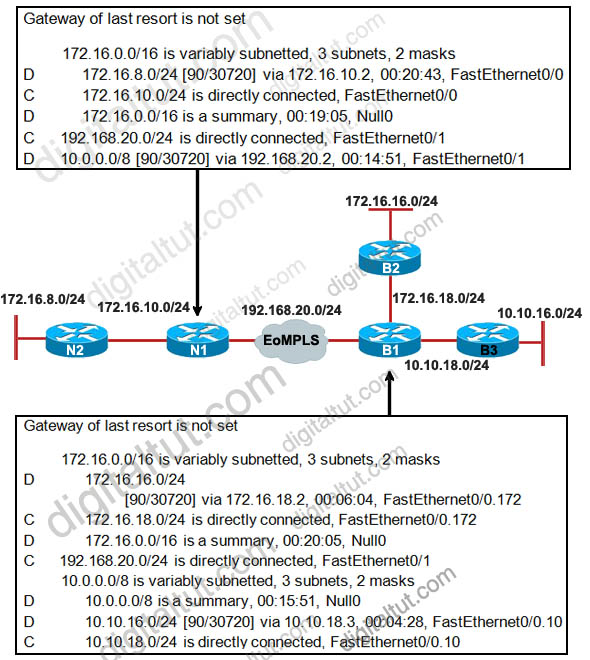 A. Traffic is flowing between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and subnets 172.16.16.0 and 10.10.16.0 and no configuration changes are needed.
A. Traffic is flowing between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and subnets 172.16.16.0 and 10.10.16.0 and no configuration changes are needed.
B. Auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and subnets 172.16.16.0 and 10.10.16.0.
C. Traffic will flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and 172.16.16.0 without any further configuration changes. However, auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and the 10.10.16.0 subnet.
D. Auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and the 172.16.16.0 subnet. However, traffic will flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and 10.10.16.0 without any further configuration changes.
Answer: B
Question 47
Refer to the exhibit. A Boston company bought the assets of a New York company and is trying to route traffic between the two data networks using EIGRP. The show command output shows that traffic will not flow between the networks. As a network consultant, you were asked to modify the configuration and certify the interoperability of the two networks. For traffic to flow from subnet 172.16.8.0/24 to the 172.16.16.0/24 subnet, which configuration change do you recommend?
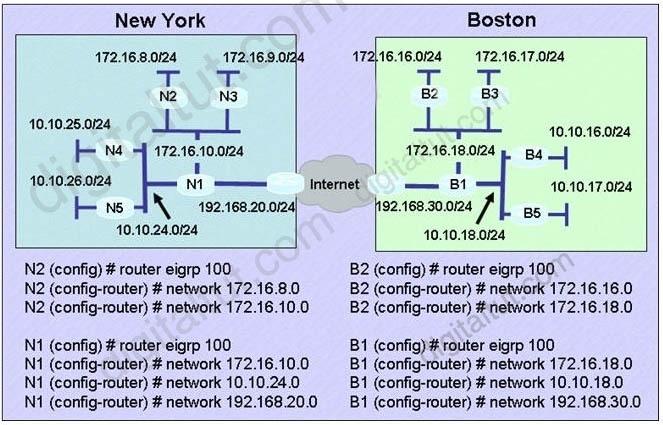 A. Turn off autosummarization on routers N1 and B1.
A. Turn off autosummarization on routers N1 and B1.
B. Add IP summary addresses to the Internet-pointing interfaces of routers N1 and B1.
C. Turn off autosummarization on routers N2 and B2.
D. Add wildcard masks to the network commands on routers N2 and B2.
Answer: A
Which three statements about the EIGRP routing protocol are true? (Choose three)
A – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.9
B – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.10
C – EIGRP supports five generic packet types. including hello, update, query, reply, and ACK packets
D – EIGRP supports five generic packet types, including hello, database description (DBD), link-state request (LSR), link-state update (LSU), and LSAck
E – E. EIGRP will form a neighbor relationship with another peer even when their K values are mismatched
F – A. EIGRP will not form a neighbor relationship with another peer when their K values are mismatched
Answer: B, C, F
Question 2
After DUAL calculations, a router has identified a successor route, but no routes have qualified as a feasible successor. In the event that the current successor goes down, what process will EIGRP use in the selection of a new successor?
A – EIGRP will find the interface with the lowest MAC address
B – The route will transition to the active state
C – The route will transition to the passive state
D – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest feasible distance (FD)
E – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest advertised distance (AD)
Answer: B
Explanation
When a route (current successor) goes down, the router first checks its topology table for a feasible successor but it can’t find one. So it goes active on the that route to find a new successor by sending queries out to its neighbors requesting a path to the lost route.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 have established a neighbor relationship and are exchanging routing information. The network design requires that R1 receive routing updates from R2, but not advertise any routes to R2. Which configuration command sequence will successfully accomplish this task?

R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
B – R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
C – R1(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
D – R2(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
E – R1(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
F – R2(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
Answer: C
Explanation
We can not use passive-interface to accomplish this task because the “passive-interface…” command (in EIGRP or OSPF) will shut down the neighbor relationship of these two routers (no hello packets are exchanged). And to filter routing updates we should configure a distribute list on R1 with an access list that deny all and apply it to the outbound direction so that R1 can receive but can not send routing updates.
Question 4
EIGRP has been configured to operate over Frame Relay multipoint connections. What should the bandwidth command be set to?
A – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection multiplied by the number of circuits
B – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection
C – the CIR rate of the highest speed connection
D – the sum of all the CIRs divided by the number of connections
Answer: A
Explanation
If the multipoint network has different speeds allocated to the VCs, take the lowest CIR and simply multiply it by the number of circuits. This is because in Frame-relay all neighbors share the bandwidth equally, regardless of the actual CIR of each individual PVC, so we have to get the lowest speed CIR rate and multiply it by the number of circuits. This result will be applied on the main interface (or multipoint connection interface).
Question 5

A – Router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 out of interface FastEthernet0/0
B – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out before it declares the neighbor unreachable
C – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out inquiring for a second successor to network 10.6.1.0/24
D – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 in response to the query sent out about network 10.6.1.0/24
Answer: D
Explanation
From the output, we notice that there is an active route (A) and the reply status flag (r) was set. An active EIGRP route is the state when a network change occurs and a feasible successor is not found by a EIGRP router for a given route (10.6.1.0/24); and the reply status flag (r) means that R1′s queries were sent out to the neighbors asking for routing information to the 10.6.1.0/24 network but hasn’t received a reply yet. Therefore the answer A – router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 is not correct because router R1 can’t find a path to that network. Answers B and C are not correct because R1 doesn’t send a hello message but a query asking for routing information to the desired network.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on all routers in the network. What additional configuration statement should be included on router R4 to advertise a default route to its neighbors?

B. R4(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
C. R4(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
D. R4(config-router)# default-information originate
Answer: A
Explanation
The “ip default-network ” command will direct other routers to send its unknown traffic to this network. Other router (R1,R2,R3) will indicate this network as the “Gateway of last resort”.
There is another way to route unknown traffic to 10.1.1.0/24 network: create a static route using “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2″ command then inject this route using the “network 0.0.0.0″ command, or using “redistribute static” command.
Note: In EIGRP, default routes cannot be directly injected (as they can in OSPF with the default-information originate command. Also, EIGRP does not have the “default-information originate” command).
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC are not receiving each other’s routes. What is the solution?

B. Issue the no ip split horizon command on router RTA.
C. Configure subinterfaces on the spoke routers and assign different IP address subnets for each subinterface.
D. Check and change the access lists on router RTA.
E. Issue the no ip split horizon eigrp 1 command on router RTA.
Answer: E
Explanation
RTB and RTC cannot see each other because of the split horizon rule: “A router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. To overcome this problem we can configure subinterfaces or disable split horizon with the command “no ip split horizon eigrp 1″ on RTA.
Question 8
When troubleshooting an EIGRP connectivity problem, you notice that two connected EIGRP routers are not becoming EIGRP neighbors. A ping between the two routers was successful. What is the next thing that should be checked?
A. Verify that the EIGRP hello and hold timers match exactly.
B. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP peer command.
C. Verify that EIGRP broadcast packets are not being dropped between the two routers with the show ip EIGRP traffic command.
D. Verify that EIGRP is enabled for the appropriate networks on the local and neighboring router.
Answer: D
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. You are the network administrator of the Route.com company. You have been tasked to implement a hub and spoke EIGRP topology over Frame Relay to provide connectivity between the networks at headquarters and all 300 spokes.
Before you begin the actual implementation, which three pieces of information are more important to know than the others? (Choose three)

B. the Cisco IOS version running on all the routers
C. the router model number of all the spoke routers
D. the number of HQ networks connected behind the headquarter routers
E. the routing policy, such as whether or not the spokes can be used as backup transient point between the two headquarter routers
Answer: A B E
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. The Route.com company is running EIGRP between all the routers. Currently, if one of the LAN links (LAN1 or LAN2) at the headquarters flaps (goes up and down), the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers will experience high CPU usage and have a long EIGRP convergence time. As the new network administrator, you are asked to investigate this situation and determine if there is a quick way to resolve this issue.
Which is the most important thing that you can quickly verify first to resolve this issue?

B. Verify that the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers are configured to send only a default route to all the spoke routers.
C. Verify that the HQ-RTR1 and HQ-RTR2 routers are configured for EIGRP Nonstop Forwarding.
D. Verify that all the spoke routers are configured for autosummarization.
E. Verify that all the spoke routers are configured as EIGRP stub.
Answer: E
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. When you examine the routing table of R1 and R4, you are not able to see the R1 Ethernet subnet on the R4 routing table. You are also not able to see the R4 Ethernet subnet on the R1 routing table.
Which configuration change should be made to resolve this issue? Select the routers where the configuration change will be required, and select the required EIGRP configuration command(s). (Choose two)

B. R2 and R3
C. ip summary-address eigrp 1 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 and ip summary-address eigrp 1
D. variance 2
E. eigrp stub connected
F. no auto-summary
Answer: B F
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit. The actual speed of the serial links between R2 and R3 are 256 kb/s and 512 kb/s respectively. When configuring EIGRP on routers R2 and R3, the network administrator configured the bandwidth of both serial interfaces to 512 kb/s. What will be the effect?

B. The interface “delay” value used in the EIGRP metric calculation will be inaccurate on the 256 kb/s serial interface.
C. The amount of bandwidth used for EIGRP routing protocol traffic on the 256 kb/s link can become excessive.
D. EIGRP can load balance between the two serial links only if the variance is set to 2 or higher.
E. Unequal cost load balancing will be disabled.
Answer: C
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com has just implemented this EIGRP network. A network administrator came to you for advice while trying to implement load balancing across part of their EIGRP network.
If the variance value is configured as 2 on all routers and all other metric and K values are configured to their default values, traffic from the Internet to the data center will be load balanced across how many paths?

B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: C
Explanation
First we should list all the paths from the Internet to the data center:
+ A-B-C-H with a metric of 70 (40 + 15 + 15)
+ A-B-E-H with a metric of 60 (40+10+10)
+ A-D-E-H with a metric of 30 (10+10+10)
+ A-D-E-B-C-H with a metric of 60 (10+10+10+15+15)
+ A-D-E-F-G-H with a metric of 70 (10+10+10+20+20)
+ A-F-G-H with a metric of 60 (20+20+20)
+ A-F-E-H with a metric of 40 (20+10+10)
So the path A-D-E-H will be chosen because it has the best metric. But EIGRP can support unequal cost path load balancing. By configuring the variance value of 2, the minimum metric is increased to 60 (30 * 2) and all the routes that have a metric of less than or equal to 60 and satisfy the feasibility condition will be used to send traffic.
Besides the main path A-D-E-H we have 4 more paths that have the metric of less than or equal to 60 (we also include the Advertised Distances of these routes for later comparison):
+ A-B-E-H with an AD of 20
+ A-D-E-B-C-H with an AD of 50
+ A-F-G-H with an AD of 40
+ A-F-E-H with an AD of 20
Now the last thing we need to consider is the feasible condition. The feasible condition states:
“To qualify as a feasible successor, a router must have an AD less than the FD of the current successor route”
The FD of the current successor route here is 30 (notice that the variance number is not calculated here). Therefore there are only 2 paths that can satisfy this conditions: the path A-B-E-H & A-F-E-H.
In conclusion, traffic from the Internet to the data center will be load balanced across 3 paths, including the main path (successor path) -> C is correct.
Question 14
Which condition must be satisfied before an EIGRP neighbor can be considered a feasible successor?
A. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be less than or equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
B. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be less than the feasible distance of the current successor.
C. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be greater than the feasible distance of the current successor.
D. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
E. The neighbor’s advertised distance must be greater than or equal to the feasible distance of the current successor.
Answer: B
Explanation
As explained in question 1, this is called the feasible condition.
Question 15
Which statement about a non-zero value for the load metric (k2) for EIGRP is true?
A. A change in the load on an interface will cause EIGRP to recalculate the routing metrics and send a corresponding update out to each of its neighbors.
B. EIGRP calculates interface load as a 5-minute exponentially weighted average that is updated every 5 minutes.
C. EIGRP considers the load of an interface only when sending an update for some other reason.
D. A change in the load on an interface will cause EIGRP to recalculate and update the administrative distance for all routes learned on that interface.
Answer: C
Explanation
The load metric (k2) represents the worst load on a link between source and destination.
EIGRP routing updates are triggered only by a change in network topology (like links, interfaces go up/down, router added/removed), and not by change in interface load or reliability -> A & D are not correct.
The load is a five minute exponentially weighted average that is updated every five seconds (not five minutes) -> B is not correct.
EIGRP considers the load of an interface only when sending an update for some other reason (like a link failure, topology change). Updates are not sent out each time the load changes -> C is correct.
Note: To learn how to calculate EIGRP metric, please read my EIGRP tutorial – Part 3.
Question 16
Your network consists of a large hub-and-spoke Frame Relay network with a CIR of 56 kb/s for each spoke.
Which statement about the selection of a dynamic protocol is true?
A. EIGRP would be appropriate if LMI type ANSI is NOT used.
B. EIGRP would be appropriate, because the Frame Relay spokes could be segmented into their own areas.
C. EIGRP would be appropriate, because by default, queries are not propagated across the slow speed Frame Relay links.
D. EIGRP would be appropriate, because you can manage how much bandwidth is consumed over the Frame Relay interface.
Answer: D
Explanation
By default, EIGRP will limit itself to using no more than 50% of the interface bandwidth. The primary benefit of controlling EIGRP’s bandwidth usage is to avoid losing EIGRP packets, which could occur when EIGRP generates data faster than the interface line can absorb it. This is of particular benefit on Frame Relay networks, where the access interface bandwidth and the PVC capacity may be very different.
For example, in our Frame Relay topology a Hub is connected with 4 Spoke routers. The main Frame Relay interface on Hub router is 512Kpbs which is not enough to use for 6 links of 128 Kbps ( = 768 Kbps).

Hub(config)#interface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point
Hub(config-subif)#bandwidth 85
Also on Spoke routers we need to set this value. For example on Spoke1:
Spoke1(config)#interface Serial0/1.0 point-to-point
Spoke1(config-subif)#bandwidth 85
Notice that by default, EIGRP limits itself to use no more than 50% of the configured interface bandwidth. In this case EIGRP will not use more than 42.5 Kbps (50% of 85 Kbps).
Question 17
When an EIGRP topology change is detected, what is the correct order of events when there is a FS?
A.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
The feasible route is used.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
B.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used.
C.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used.
DUAL is notified.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
D.
DUAL is notified.
The neighbor adjacency is deleted.
Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
The feasible route is used.
Answer: D
Question 18
Refer to the exhibit. You want to use all the routes in the EIGRP topology for IP load balancing.

Which two EIGRP subcommands would you use to accomplish this goal? (Choose two)
A. traffic-share balanced
B. distance
C. maximum-paths
D. default-network
E. variance
Answer: C E
Explanation
Notice that the “maximum-paths” command is used to share traffic to equal cost path while the “variance” command can share traffic to unequal cost path.
In the output above we learn that EIGRP is using 2 successors to send traffic. By using the “variance 2″ command we can share traffic to other feasible successor routes. But by default, EIGRP only shares traffic to 4 paths. So we need to use the “maximum-paths 6″ to make sure all of these routes are used.
Question 19
Refer to the exhibit. R1 accesses the Internet using E0/0. You have been asked to configure R1 so that a default route is generated to its downstream devices (191.0.0.1 and 192.0.0.1). Which commands would create this configuration?

A.
router eigrp 190
redistribute static
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0
B. ip default-network 20.0.0.0
C.
router eigrp 190
redistribute static
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 Null0
D. ip default-network 20.20.20.0
Answer: A
Question 20
Which command will display EIGRP packets sent and received, as well as statistics on hello packets, updates, queries, replies, and acknowledgments?
A. debug eigrp packets
B. show ip eigrp traffic
C. debug ip eigrp
D. show ip eigrp interfaces
Answer: B
Explanation
Below is the output of the “show ip eigrp traffic” command:

Question 21
Which three statements are true about EIGRP operation? (Choose three)
A. When summarization is configured, the router will also create a route to null 0.
B. The summary route remains in the route table, even if there are no more specific routes to the network.
C. Summarization is configured on a per-interface level.
D. The maximum metric for the specific routes is used as the metric for the summary route.
E. Automatic summarization across major network boundaries is enabled by default.
Answer: A C E
Question 22
Which two statements about the EIGRP DUAL process are correct? (Choose two)
A. An EIGRP route will go active if there are no successors or feasible successors in the EIGRP topology table.
B. An EIGRP route will go passive if there are no successors in the EIGRP topology table.
C. DUAL will trigger an EIGRP query process while placing the flapping routes in the holddown state.
D. A feasible successor in the EIGRP topology table can become the successor only after all the query requests have been replied to.
E. The stuck in active state is caused when the wait for the query replies have timed out.
F. EIGRP queries are sent during the loading state in the EIGRP neighbor establishment process.
Answer: A E
Question 23
What are three key concepts that apply when configuring the EIGRP stub routing feature in a hub and spoke network? (Choose three)
A. A hub router prevents routes from being advertised to the remote router.
B. Only remote routers are configured as stubs.
C. Stub routers are not queried for routes.
D. Spoke routers connected to hub routers answer the route queries for the stub router.
E. A stub router should have only EIGRP hub routers as neighbors.
F. EIGRP stub routing should be used on hub routers only.
Answer: B C E
Question 24
Which three statements are true about EIGRP route summarization? (Choose three)
A. Manual route summarization is configured in router configuration mode when the router is configured for EIGRP routing.
B. Manual route summarization is configured on the interface.
C. When manual summarization is configured, the summary route will use the metric of the largest specific metric of the summary routes.
D. The ip summary-address eigrp command generates a default route with an administrative distance of 90.
E. The ip summary-address eigrp command generates a default route with an administrative distance of 5.
F. When manual summarization is configured, the router immediately creates a route that points to null0 interface
Answer: B E F
Explanation
The ip summary-address eigrp {AS number} {address mask} command is used to configure a summary aggregate address for a specified interface. For example with the topology below:

R2(config)#interface fa0/0
R2(config-if)#ip summary-address eigrp 1 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.248
This configuration causes EIGRP to summarize network 1.1.1.0 and sends out Fa0/0 interface
After configuring manual EIGRP summary, the routing table of the local router will have a route to Null0:

So why is this route inserted in the routing table when doing summarization? Well, you may notice that although our summarized subnet is 1.1.1.0/29 but we don’t have all IP addresses in this subnet. Assignable IP addresses of subnet 1.1.1.0/29 are from 1.1.1.1 to 1.1.1.6. Imagine what happens if R1 sends a packet to 1.1.1.6. Because R1 do believe R2 is connected with this IP so it will send this packet to R2. But R2 does not have this IP so if R2 has a default-route to R1 (for example R1 is connected to the Internet and R2 routes all unknown destination IP packets to R1) then a loop will occur.
To solve this problem, some routing protocols automatically add a route to Null0. A packet is sent to “Null0″ means that packet is dropped. Suppose that R1 sends a packet to 1.1.1.6 through R2, even R2 does not have a specific route for that IP, it does have a general route pointing to Null0 which the packet sent to 1.1.1.6 can be matched -> That packet is dropped at R2 without causing a routing loop!
By default, EIGRP summary routes are given an administrative distance value of 5. Notice that this value is only shown on the local router doing the summarization. On other routers we can still see an administrative distance of 90 in their routing table.

Question 25
After implementing EIGRP on your network, you issue the show ip eigrp traffic command on router C. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IF-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 481/444
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Approximately 25 minutes later, you issue the same command again. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 1057/1020
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Approximately 25 minutes later, you issue the same command a third time. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 1754/1717
Updates sent/received: 41/32
Queries sent/received: 5/1
Replies sent/received: 1/4
Acks sent/received: 21/25
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
What can you conclude about this network?
A. The network has been stable for at least the last 45 minutes.
B. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C knows an alternate path to the network.
C. There is a flapping link or interface, and router A does not know an alternate path to the network.
D. EIGRP is not working correctly on router C.
E. There is not enough information to make a determination.
Answer: A
Explanation
In three times using the command, the “Queries sent/received” & “Replies sent/received” are still the same -> the network is stable.
Question 26
After implementing EIGRP on your network, you issue the show ip eigrp traffic command on router C. The following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2112/2076
Updates sent/received: 47/38
Queries sent/received: 5/3
Replies sent/received: 3/4
Acks sent/received: 29/33
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Moments later, you issue the same command a second time and the following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2139/2104
Updates sent/received: 50/39
Queries sent/received: 5/4
Replies sent/received: 4/4
Acks sent/received: 31/37
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Moments later, you issue the same command a third time and the following output is shown:
RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1
Hellos sent/received: 2162/2126
Updates sent/received: 53/42
Queries sent/received: 5/5
Replies sent/received: 5/4
Acks sent/received: 35/41
Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
What information can you determine about this network?
A. The network is stable.
B. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C knows an alternate path to the network.
C. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C does not know an alternate path to the network.
D. EIGRP is not working correctly on router C.
E. There is not enough information to make a determination.
Answer: B
Explanation
We notice that the “Queries received” number is increased so router C has been asked for a route. The “Replies sent” number is also increased -> router C knows an alternate path to the network.
Question 27
R1 and R2 are connected and are running EIGRP on all their interfaces, R1 has four interfaces, with IP address 172.16.1.1/24, 172.16.2.3/24,172.16.5.1/24, and 10.1.1.1/24. R2 has two interfaces, with IP address 172.16.1.2/24 and 192.168.1.1/24. There are other routers in the network that are connected on each of the interfaces of these two routers that are also running EIGRP. Which summary routes does R1 generate automatically (assuming auto-summarization is enable)? (choose two)
A. 192.168.1.0/24
B. 10.0.0.0/8
C. 172.16.1.0/22
D. 172.16.0.0/16
E. 10.1.1.0/24
Answer: B D
Question 28

A. R1—R2—R6
B. R1—R3—R6
C. R1—R4—R6
D. R1—R5—R6
Answer: C D
Question 29
What does the default value of the EIGRP variance command of 1 mean?
A. Load balancing is disabled on this router.
B. The router performs equal-cost load balancing.
C. Only the path that is the feasible successor should be used.
D. The router only performs equal-cost load balancing on all paths that have a metric greater than 1.
Answer: B
Question 30
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on all routers in the network. The command metric weights 0 0 1 0 0 has been added to the EIGRP process so that only the delay metric is used in the path calculations. Which router will R1 select as the successor and feasible successor for Network A?

B. R4 becomes the successor for Network A and will be included in the routing table. No feasible successor will be selected as the advertised distance from R2 is higher than the feasible distance.
C. R2 becomes the successor and will be placed in the routing table. R4 becomes the feasible successor for Network A.
D. R2 becomes the successor and will be placed in the routing table. No feasible successor will be selected as the reported distance from R4 is lower than the feasible distance.
Answer: B
Question 31
Based on the exhibited output, which three statements are true? (Choose three)

A. R1 is in AS 200.
B. R1 will load balance between three paths to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix because all three paths have the same advertised distance (AD) of 40512000.
C. The best path for R1 to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix is via 192.168.1.66.
D. 40512000 is the advertised distance (AD) via 192.168.1.66 to reach the 192.168.1.48/28 prefix.
E. All the routes are in the passive mode because these routes are in the hold-down state.
F. All the routes are in the passive mode because R1 is in the query process for those routes.
Answer: A C D
Explanation
In the statement “IP-EIGRP Topology Table for process 200″, process 200 here means AS 200 -> A is correct.
There are 3 paths to reach network 192.168.1.48/28 but there is only 1 path in the routing table (because there is only 1 successor) so the path with least FD will be chosen -> path via 192.168.1.66 with a FD of 40537600 will be chosen -> C is correct.
The other parameter, 40512000, is the AD of that route -> D is correct.
Question 32
Characteristics of the routing protocol EIGRP? (choose two)
A. Updates are sent as broadcast.
B. Updates are sent as multicast.
C. LSAs are sent to adjacent neighbors.
D. Metric values are represented in a 32-bit format for granularity.
Answer: B D
Explanation
EIGRP updates are sent as multicast to address 224.0.0.10 -> B is correct.
EIGRP metric values, for example an entry in the “show ip route” command:
D 10.1.21.128/27 [90/156160] via 10.1.4.5, 00:00:21, FastEthernet1/0/1
EIGRP metric here is 156160 and it is a 32-bit value.
Question 33
Which EIGRP packet statement is true?
A. On high-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 5 seconds for neighbor discovery.
B. On low-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 15 seconds for neighbor discovery.
C. Reply packets are multicast to IP address 224.0.0.10 using RTP.
D. Update packets route reliable change information only to the affected routers.
E. Reply packets are used to send routing updates.
Answer: D
Question 34
Which three descriptions are correct based on the exhibited output? (Choose three)

B. The route to 10.2.0.0/16 was redistributed into EIGRP.
C. A default route has been redistributed into the EIGRP autonomous system.
D. R1 is configured with the ip summary-address command.
Answer: A C D
Explanation
From the routing table above, we see that network 172.16.1. can be reached via 2 unequal paths (with FD of 23072000 & 20640000) so surely R1 has been configured with the “variance” command -> A is correct.
By configuring a default route and redistribute it into EIGRP you will get the line “D *EX 0.0.0.0/0 …” line in the routing table of that router -> C is correct.
From the line “10.2.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:16:18, Null0″ we know that this network has been summarized with the “ip summaray-address” command (notice that 10.2.0.0 is not the major network of net-> D is correct.
Question 35
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)

B. The eigrp stub command will automatically enable summarization of routes on R2.
C. The eigrp stub command prevents all routes except a default route from being advertised to R1.
D. Router R1 will advertise connected and summary routes only.
E. Router R1 will advertise connected and static routes. The sending of summary routes will not be permitted.
F. Router R1 is configured as a receive-only neighbor and will not send any connected, static or summary routes.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The command “eigrp stub” turns R1 into a stub router so R2 will never send any query to R1 because R2 knows that a stub router will only route packets for networks it has explicitly advertised -> A is correct.
The command “eigrp stub” is same as “eigrp stub connected summary” command because connected and summarized routes are advertised by default -> D is correct.
Note: Because the network 192.168.50.0 is not advertised by “network” statement, it is necessary to redistribute connected route with the “redistribute connected” command.
Question 36
Refer to the exhibits. Router B should advertise the network connected to the E0/0/0 interface to router A and block all other network advertisements. The IP routing table on router A indicates that it is not receiving this prefix from router B.
What is the probable cause of the problem?


B. An access list on router B is causing the 192.168.3.32/28 network to be denied.
C. The distribute list on router B is referencing a numbered access list that does not exist on router B.
D. The distribute list on router B is referencing the wrong interface.
Answer: A
Explanation
This is an unclear question. The question says “Router B should advertise the network connected to the E0/0/0 interface to router A and block all other network advertisements. The IP routing table on router A indicates that it is not receiving this prefix from router B.” That means the network 192.168.3.16/28 (including the IP 192.168.3.21/28) is not received on router A -> A is the most suitable answer.
Note: Distribute list are used to filter routing updates and they are based on access lists.
Question 37
Study the exhibit carefully. What must be done on router A in order to make EIGRP work effectively in a Frame Relay multipoint environment?

B. Issue the command bandwidth 56 on each subinterface.
C. Issue the command bandwidth 224 on each subinterface.
D. Issue the command bandwidth 224 on the physical interface.
Answer: D
Explanation
In Frame Relay, all neighbors share the same bandwidth, regardless of the actual CIR of each individual PVC. In this case the CIR of each PVC is the same so we can find the bandwidth of the main interface (multipoint connection interface) by 56 x 4 = 224.
Notice that if the bandwidth on each PVC is not equal then we get the lowest bandwidth to multiply.
Question 38
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE Enterprises has many stub networks in their enterprise network, such as router B and its associated network. EIGRP is to be implemented on router A so that neither the prefix for the S/0/0/0 interface nor the prefixes from router B appear in the routing tables for the router in the enterprise network.
Which action will accomplish this goal?

B. Use the passive-interface command for interface Serial0/0/0.
C. Use a mask with the network command to exclude interface Serial0/0/0.
D. Implement a distribute list to exclude the link prefix from the routing updates.
Answer: C
Explanation
If we declare router B a stub router then the routers in Enterprise Network still learn about the network for S0/0/0 interface and the network behind router B -> A is not correct.
If we use the passive-interface command on s0/0/0 interface then router A & B can not become neighbor because they don’t exchange hello messages -> A can not send traffic to the network behind B -> B is not correct.
Theoretically, we can use a distribute list to exclude both the link prefix and the prefix from router B but it is not efficient because:
+ We have many stub networks so we will need a “long” distribute list.
+ We declare networks in stub routers (like router B) while filter them out at router A -> it is a waste.
I am not totally sure about answer C because if we “use a mask with the network command to exclude interface Serial0/0/0″ then router A and B can not become neighbors and the situation is same as answer B. But from many discussions about this question, maybe C is the best answer.
Question 39
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured with the default configuration on all routers. Autosummarization is enabled on routers R2 and R3, but it is disabled on router R1. Which two EIGRP routes will be seen in the routing table of router R3? (Choose two)

B. 10.10.0.0/16
C. 10.10.10.0/24
D. 172.16.0.0/16
E. 172.16.0.0/24
F. 172.16.10.0/24
Answer: C D
Explanation
EIGRP performs an auto-summarization each time it crosses a border between two different major networks. In this case all different networks are in different major networks so EIGRP will perform auto-summarization when it exits an interface. But R1 has been configured with “no auto-summary” command so EIGRP will not summarize on S0 interface of R1. So the routing table of R2 will have the network 10.10.10.0/24 (not be summarized).
When exiting S1 interface of R2, EIGRP summarizes network 172.16.10.0/24 into the major 172.16.0.0/16 network but it does not summarize network 10.10.10.0/24 because it is not directly connected with this network. Therefore in the routing table of R3 there will have:
+ Network 10.10.10.0/24 ( not summarized)
+ Network 172.16.0.0/16 (summarized)
-> C and D are correct.
Note: I simulated this question on GNS3, you can see the final outputs of the “show ip route” commands on these routers (I connected these routers via FastEthernet, not Serial interfaces so the outputs are slightly different but the main points are not changed).



Question 40
Refer to the exhibit. In a redundant hub-and-spoke deployment using EIGRP, what feature can be used to ensure that routers C through F are not used as transit routers for data traveling from router B to network 10.1.1.0?

B. Use the EIGRP Stub feature on routers C, D, E, and F.
C. Use passive-interface on the spoke links in routers A and B.
D. Change the administrative distance in routers A and B for routes learned from routers Cr D. E, and F.
Answer: B
Explanation
By configuring “stub” feature on routers C D E and F, routers A and B will not try to transit traffic through these routers. For example, if the network connecting from routers A and B is down, router B will not send to network 10.1.1.0/24 from router B -> routerC/D/E/F -> router A -> network 10.1.1.0/24.
Question 41
Refer to the exhibit. How would you confirm on R1 that load balancing is actually occurring on the default-network (0.0.0.0)?

A. Use ping and the show ip route command to confirm the timers for each default network resets to 0.
B. Load balancing does not occur over default networks; the second route will only be used for failover.
C. Use an extended ping along with repeated show ip route commands to confirm the gateway of last resort address toggles back and forth.
D. Use the traceroute command to an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Answer: D
Explanation
The most simple method to test load balancing is to use the “traceroute” command. If load balancing is working correctly, we will see different paths to reach the destination each time we use that command.
Unknown address will be routed via the default-network 0.0.0.0 so we must use an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Question 42
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com is planning to implement load balancing for traffic between host on the 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20./24 networks. You have been asked to review the implementation plan for this project. Which statement about the plan is true?

B. It should include a task to configure EIGRP multipath equal to 2 on R1 and R4.
C. It should include a task to implement OSPF because it handles unequal cost load balancing most efficiently using variance.
D. It should include a task that establishes a baseline before and after the configuration has been changed.
Answer: D
Explanation
A complete implementation plan should be:
1. Configure variance on R1 and R4
2. Use traceroute to validate load balancing has been activated
3. Document configuration changes
4. Establish a new traffic throughput baseline
5. Compare the new and old baselines and verify that load balancing is implemented as desired.
Question 43
Refer to the exhibit. ROUTE.com is planning to implement load balancing for traffic between host on the 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20./24 networks. You have been asked to review the implementation plan for this project. Which statement about the plan is true?

B. It should include a task to configure multipath to equal a value of 2 on R1 and R4.
C. It should use a ping instead of a traceroute to validate that load balancing has been activated.
D. It should contain a task that documents the changes made to the configurations.
Answer: D
Question 44
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP had converged in AS 1 when the link between router R1 and R2 went down. The console on router R2 generated the following messages:
| *Mar 20 12:12:06: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP 1: Neighbor 10.1.4.3 (Serial0) is down: stuck in active *Mar 20 12:15:23: %DUAL-3-SIA: Route 10.1.1.0/24 stuck-in-active state in IP-EIGRP 1. Cleaning up |

B. Incorrect bandwidth configuration on router R5 prevents R2 from establishing neighbor adjacency.
C. Router R3 did not reply to the query about network 10.1.1.0/24 sent by router R2.
D. Router R5 did not reply to the query about network 10.1.1.0/24 sent by router R2.
Answer: C
Explanation
When the link between R1 and R2 is down, R2 loses its successor for the network 10.1.1.0/24. R2 checks its topology table for a feasible successor but it can’t find one. So R2 goes active on the that route to find a new successor by sending queries out to its neighbors (R3 and R5) requesting a path to the lost route. Both R3 and R5 also go “active” for the that route. But R5 doesn’t have any neighbor to ask besides R2 so it will send an “unreachable message” to indicate it has no alternative path for that route and has no other neighbor to query. R3 also checks its EIRGP topology table for a feasible successor but it has none, too. Unlike R5, R3 has a neighbor (R4) so it continues to query this router.
Now suppose there is a problem on the link between R3 and R4 so R4 never receives the query from R3 and of course, R3 also never receives a reply back from R4. Therefore, R3 can’t reply back to R2. After about 3 minutes, the “Stuck in active” (SIA) timer on R2 expires and R2 marks the route 10.1.1.0/24 as “stuck in active” route.
The output line “via 10.1.3.3 (Infinity/Infinity), r, Seiral0, serno 1232″ indicates R2 has sent a query to 10.1.3.3 and is waiting for a reply (the lowercase r) -> C is correct.
Question 45
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on routers R1 and R2. However, R1 does not show R2 as a neighbor and does not accept routing updates from R2. What could be the cause of the problem?

B. Interface E0 on router R1 has not been configured with a secondary IP address of 10.1.2.1/24.
C. EIGRP cannot exchange routing updates with a neighbor’s router interface that is configured with two IP addresses.
D. EIGRP cannot form neighbor relationship and exchange routing updates with a secondary address.
Answer: D
Explanation
EIGRP updates always use the primary IP address of the outgoing interface as the source address. In this case R2 will use the 10.1.2.2/24 address, which is not in the same subnet of R1, to send EIGRP update to R1. Therefore R1 does not accept this update and generates the “not on common subnet” error message.
Answer D is a bit unclear. It should state that “EIGRP cannot form neighbor relationship and exchange routing updates if the two primary addresses on two routers are not in the same subnet”.
Notice that although R1 does not accept R2 as its EIGRP neighbors but R2 accepts R1 as its EIGRP neighbor accepts R1 hello packets..
Question 46
Refer to the exhibit. A Boston company bought the assets of a New York company and is trying to route traffic between the two data networks using EIGRP over EoMPLS. As a network consultant, you were asked to verify the interoperability of the two networks.
From the show ip route command output, what can you tell the customer about the traffic flow between the subnet in New York (172.16.8.0/24) and the subnets in Boston (172.16.16.0/24 and 10.10.16.0/24)?

B. Auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and subnets 172.16.16.0 and 10.10.16.0.
C. Traffic will flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and 172.16.16.0 without any further configuration changes. However, auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and the 10.10.16.0 subnet.
D. Auto-summary must be disabled on N1 and B1 before traffic can flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and the 172.16.16.0 subnet. However, traffic will flow between the 172.16.8.0 subnet and 10.10.16.0 without any further configuration changes.
Answer: B
Question 47
Refer to the exhibit. A Boston company bought the assets of a New York company and is trying to route traffic between the two data networks using EIGRP. The show command output shows that traffic will not flow between the networks. As a network consultant, you were asked to modify the configuration and certify the interoperability of the two networks. For traffic to flow from subnet 172.16.8.0/24 to the 172.16.16.0/24 subnet, which configuration change do you recommend?

B. Add IP summary addresses to the Internet-pointing interfaces of routers N1 and B1.
C. Turn off autosummarization on routers N2 and B2.
D. Add wildcard masks to the network commands on routers N2 and B2.
Answer: A
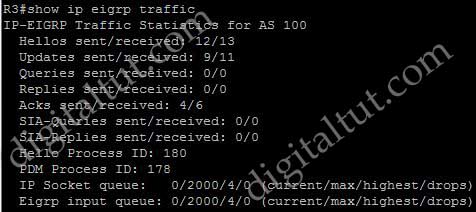
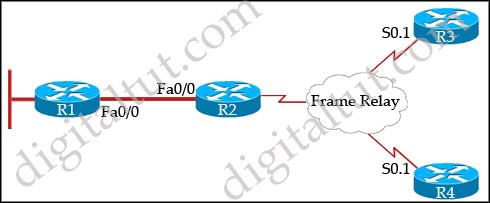
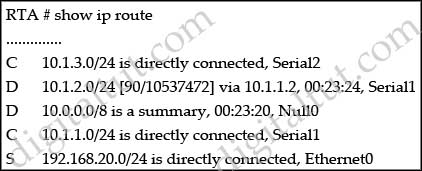
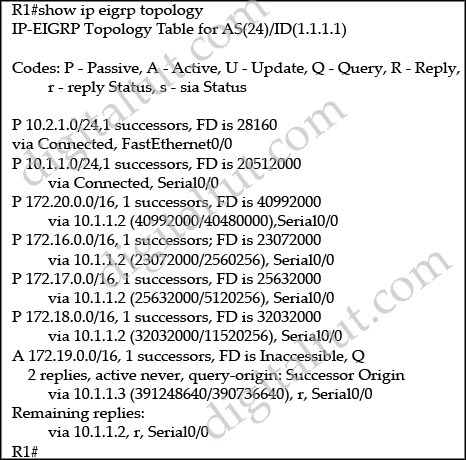
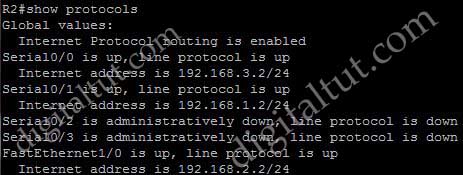
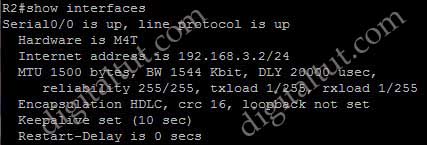
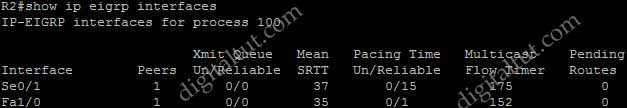
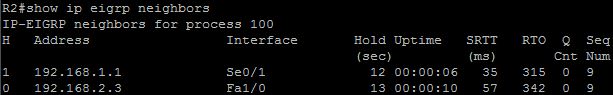
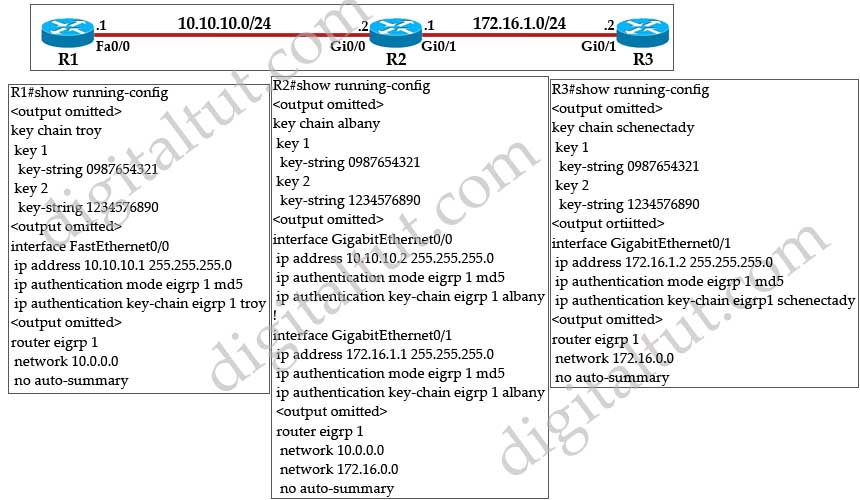

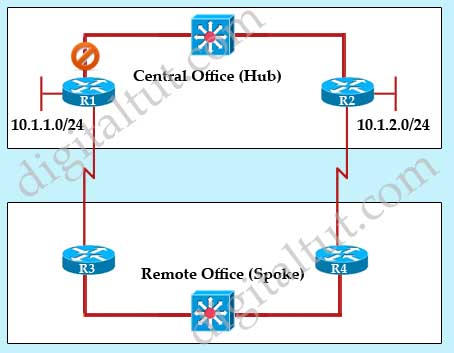
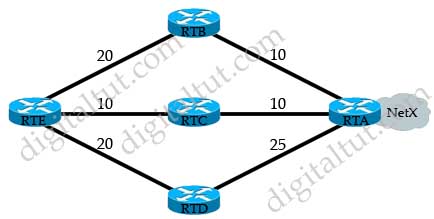
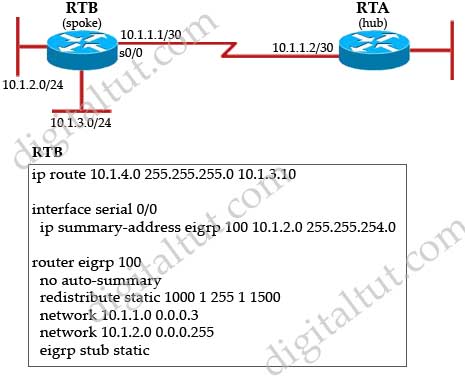
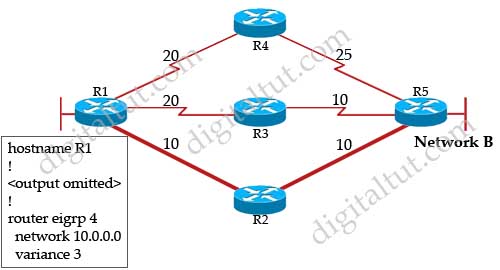
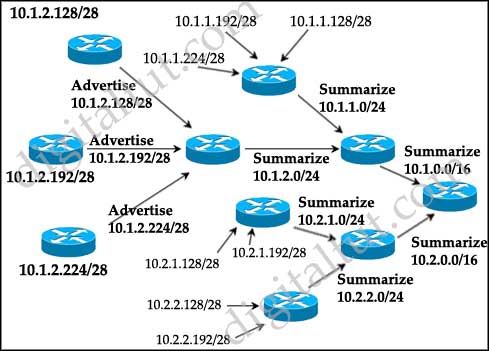
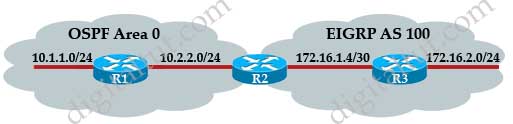
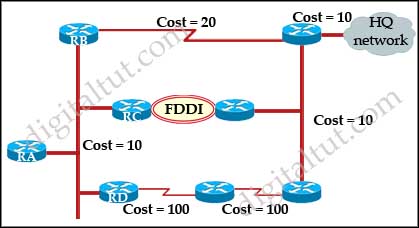
Comment