Question 1
Which command would you use on a Cisco router to verify the Layer 3 path to a host?
A. traced address
B. traceroute address
C. telnet address
D. ssh address
Answer: B
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “ping” commands. But the difference between these 2 commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. The “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC -> B is correct.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit:
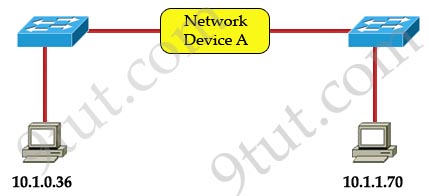
Which three statements correctly describe Network Device A? (Choose three)
A. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.128, each interface does not require an IP address.
B. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.128, each interface does require an IP address on a unique IP subnet.
C. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.0, must be a Layer 2 device for the PCs to communicate with each other.
D. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.0, must be a Layer 3 device for the PCs to communicate with each other.
E. With a network wide mask of 255.255.254.0, each interface does not require an IP address.
Answer: B D E
Explanation
The principle here is if the subnet mask makes two IP addresses 10.1.0.36 and 10.1.1.70 in the same subnet then the Network device A does not need to have IP addresses on its interfaces (and we don’t need a Layer 3 device here).
A quick way to find out the correct answers is notice that all 255.255.255.x subnet masks will separate these two IP addresses into two separate subnets so we need a Layer 3 device here and each interface must require an IP address on a unique IP subnet -> A, C are not correct while B, D are correct.
With 255.255.254.0 subnet mask, the increment here is 2 in the third octet -> the first subnet is from 10.1.0.0 to 10.1.1.255, in which two above IP addresses belong to -> each interface of Network device A does not require an IP address -> E is correct.
Question 3
What are three reasons that an organization with multiple branch offices and roaming users might implement a Cisco VPN solution instead of point-to-point WAN links? (Choose three)
A. reduced cost
B. better throughput
C. broadband incompatibility
D. increased security
E. scalability
F. reduced latency
Answer: A D E
Question 4
What two things will a router do when running a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. Send periodic updates regardless of topology changes.
B. Send entire routing table to all routers in the routing domain.
C. Use the shortest-path algorithm to the determine best path.
D. Update the routing table based on updates from their neighbors.
E. Maintain the topology of the entire network in its database.
Answer: A D
Question 5
What is the purpose of the inverse ARP?
A. to map a known DLCI to an IP address
B. to map a known IP address to a MAC address
C. to map known SPID to a MACaddress
D. to map a known DLCI to a MAC address
E. to map a known IP address to a SPID.
F. to map a known MAC address to an IP address
Answer: A
Explanation
For more information about Inverse ARP, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 6
The network shown in the diagram is experiencing connectivity problems. Which of the following will correct the problems? (Choose two.)
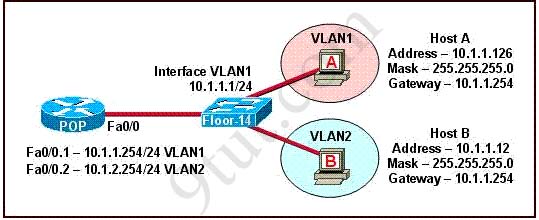
A. Configure the gateway on Host A as 10.1.1.1.
B. Configure the gateway on Host B as 10.1.2.254.
C. Configure the IP address of Host A as 10.1.2.2.
D. Configure the IP address of Host B as 10.1.2.2.
E. Configure the masks on both hosts to be 255.255.255.224.
F. Configure the masks on both hosts to be 255.255.255.240.
Answer: B D
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. For what two reasons has the router loaded its IOS image from the location that is shown? (Choose two)
A. Router1 has specific boot system command that instruct it to load IOS from TFTP server.
B. Router1 is acting as a TFTP server for other routers.
C. Router1 cannot locate a valid IOS image in flash memory.
D. Router1 defaulted to ROMMON mode and loaded the IOS image from a TFTP server.
E. Cisco routers will first attempt to load a image from TFTP for management purposes.
Answer: A C
Explanation
When powered on, the router first checks its hardware via Power-On Self Test (POST). Then it checks the configuration register to identify where to load the IOS image from. In the output above we learn that the Configuration register value is 0×2102 so the router will try to boot the system image from Flash memory first.
But we also see a line “System image file is “tftp://112.16.1.129/hampton/nitro/c7200-j-mz”. Please notice that this line tells us the image file that the device last started. In this case it is from a TFTP server. Therefore we can deduce that the router could not load the IOS image from the flash and the IOS image has been loaded from TFTP server.
Note:
If the startup-config file is missing or does not specify a location, it will check the following locations for the IOS image:
+ Flash (the default location)
+ TFTP server
+ ROM (used if no other source is found)
Question 8
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two)
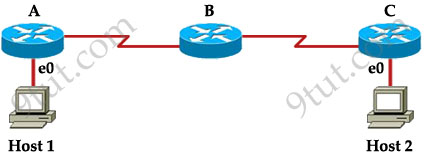
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The last known good router will try to inform you that the destination cannot be reached (with a Destination Unreachable message type) so from that information you can learn how far your packets can travel to and where the problem is.
Question 9
How is an EUI-64 format interface ID created from a 48-bit MAC address?
A. by appending 0xFF to the MAC address.
B. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFFEE.
C. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFF and appending 0xFF to it.
D. by inserting 0xFFFE between the upper three bytes and the lower three bytes of the MAC address
E. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xF and inserting 0xF after each of its first three bytes.
Answer: D
Explanation
We convert a 48-bit MAC address (IEEE 802) to a 64-bit value by breaking the MAC address into its two 24-bit halves. The first part is the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and the next part is the NIC specific part. Then the 16-bit hex value 0xFFFE is inserted between them to create a 64-bit value.
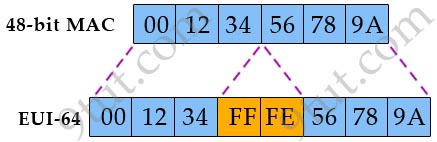
Just for your information, to obtain an IPv6 interface identifier from EUI-64 address, we have to complement the U/L bit (the seventh bit of the first byte and is used to determine whether the address is universally or locally administered). This means if it is a 1, it is set to 0; and if it is a 0, it is set to 1. In the above example, the U/L bit is 0 (from 00 = 0000 0000). Therefore we have to set this bit to 1 to create an IPv6 interface address.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit:
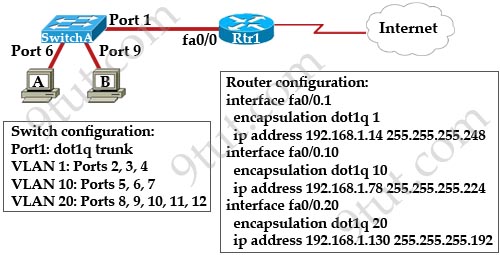
A network administrator is adding two new hosts to SwitchA. Which three values could be used for the configuration of these hosts? (Choose three)
A. host A IP address: 192.168.1.79
B. host A IP address: 192.168.1.64
C. host A default gateway: 192.168.1.78
D. host B IP address: 192.168.1.128
E. host B default gateway: 192.168.1.129
F. host B IP address: 192.168.1.190
Answer: A C F
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is asked to design a small network with redundancy. The exhibit represents this design, with all hosts configured in the same VLAN. What conclusions can be made about this design?
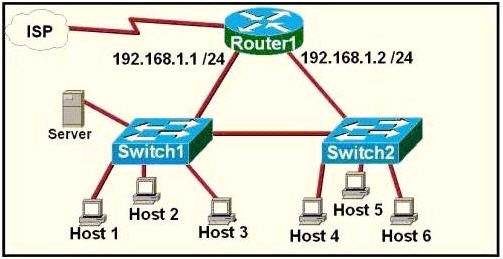
A. The design will function as intended
B. Spanning-tree will need to be used.
C. The router will not accept the addressing scheme.
D. The connection between switches should be a trunk.
E. The router interfaces must be encapsulated with the 802.1Q protocol.
Answer: C
Explanation
Each interface on a router must be in a different network. If two interfaces are in the same network, the router will not accept it and show error when the administrator assigns it.
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined about the router from the console output?
A. No configuration file was found in NVRAM.
B. No configuration file was found in flash.
C. No configuration file was found in the PCMCIA card.
D. Configuration file is normal and will load in 15 seconds.
Answer: A
Explanation
When no startup configuration file is found in NVRAM, the System Configuration Dialog will appear to ask if we want to enter the initial configuration dialog or not.
Question 13
Which command displays CPU utilization?
A. show protocols
B. show process
C. show system
D. show version
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show process” (in fact, the full command is “show processes”) command gives us lots of information about each process but in fact it is not easy to read. Below shows the output of this command (some next pages are omitted)
A more friendly way to check the CPU utilization is the command “show processes cpu history”, in which the total CPU usage on the router over a period of time: one minute, one hour, and 72 hours are clearly shown:
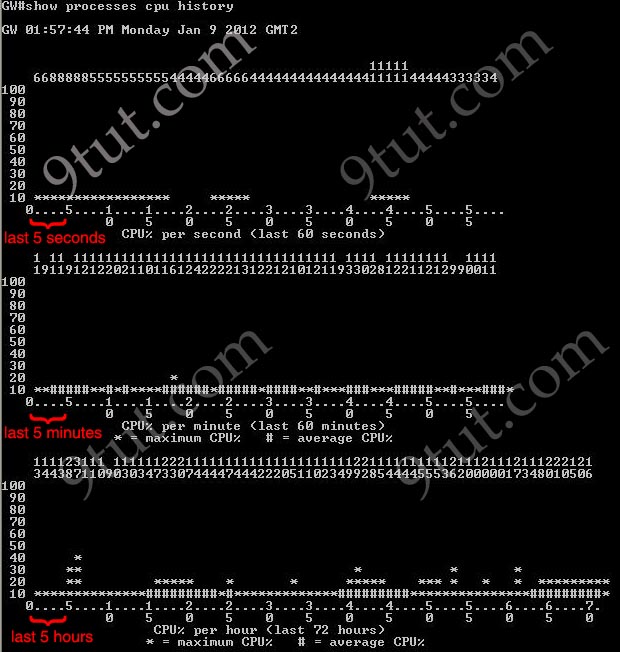
+ The Y-axis of the graph is the CPU utilization.
+ The X-axis of the graph is the increment within the period displayed in the graph
For example, from the last graph (last 72 hours) we learn that the highest CPU utilization within 72 hours is 37% about six hours ago.
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit:
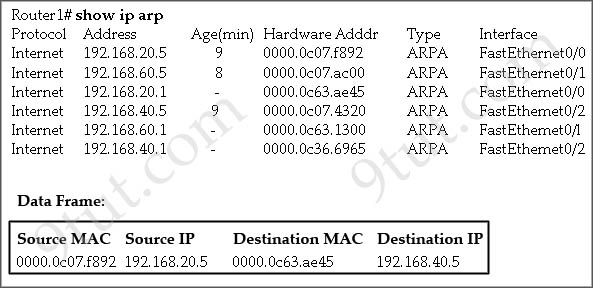
What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose three)
A. Router1 will strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c36.6965.
B. Router1 will strip off the source IP address and replace it with the IP address 192.168.40.1.
C. Router1 will strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c07.4320.
D. Router1 will strip off the destination IP address and replace it with the IP address of 192.168.40.1.
E. Router1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/1.
F. Router1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/2.
Answer: A C F
Explanation
The “Age” field in the “show ip arp” command is the age in minutes of the cache entry. A hyphen (-) means the address is local so in this case 192.168.20.1, 192.168.40.1 & 192.168.60.1 are local to this router.
From the “Data Frame”, we learn that a packet is sent to Router1 and Router1 needs to forward it to the Destination IP 192.168.40.5. Therefore this router will:
+ Strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c36.6965 (because the IP address of this interface – 192.168.40.1 is in the same subnet with the Destination IP 192.138.40.5).
+ Strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c07.4320, which is the MAC of Destination host.
+ Forward the data packet out interface FastEthemet0/2 because this interface has the IP address of 192.168.40.1.
Which command would you use on a Cisco router to verify the Layer 3 path to a host?
A. traced address
B. traceroute address
C. telnet address
D. ssh address
Answer: B
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “ping” commands. But the difference between these 2 commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. The “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC -> B is correct.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit:

Which three statements correctly describe Network Device A? (Choose three)
A. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.128, each interface does not require an IP address.
B. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.128, each interface does require an IP address on a unique IP subnet.
C. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.0, must be a Layer 2 device for the PCs to communicate with each other.
D. With a network wide mask of 255.255.255.0, must be a Layer 3 device for the PCs to communicate with each other.
E. With a network wide mask of 255.255.254.0, each interface does not require an IP address.
Answer: B D E
Explanation
The principle here is if the subnet mask makes two IP addresses 10.1.0.36 and 10.1.1.70 in the same subnet then the Network device A does not need to have IP addresses on its interfaces (and we don’t need a Layer 3 device here).
A quick way to find out the correct answers is notice that all 255.255.255.x subnet masks will separate these two IP addresses into two separate subnets so we need a Layer 3 device here and each interface must require an IP address on a unique IP subnet -> A, C are not correct while B, D are correct.
With 255.255.254.0 subnet mask, the increment here is 2 in the third octet -> the first subnet is from 10.1.0.0 to 10.1.1.255, in which two above IP addresses belong to -> each interface of Network device A does not require an IP address -> E is correct.
Question 3
What are three reasons that an organization with multiple branch offices and roaming users might implement a Cisco VPN solution instead of point-to-point WAN links? (Choose three)
A. reduced cost
B. better throughput
C. broadband incompatibility
D. increased security
E. scalability
F. reduced latency
Answer: A D E
Question 4
What two things will a router do when running a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. Send periodic updates regardless of topology changes.
B. Send entire routing table to all routers in the routing domain.
C. Use the shortest-path algorithm to the determine best path.
D. Update the routing table based on updates from their neighbors.
E. Maintain the topology of the entire network in its database.
Answer: A D
Question 5
What is the purpose of the inverse ARP?
A. to map a known DLCI to an IP address
B. to map a known IP address to a MAC address
C. to map known SPID to a MACaddress
D. to map a known DLCI to a MAC address
E. to map a known IP address to a SPID.
F. to map a known MAC address to an IP address
Answer: A
Explanation
For more information about Inverse ARP, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 6
The network shown in the diagram is experiencing connectivity problems. Which of the following will correct the problems? (Choose two.)

A. Configure the gateway on Host A as 10.1.1.1.
B. Configure the gateway on Host B as 10.1.2.254.
C. Configure the IP address of Host A as 10.1.2.2.
D. Configure the IP address of Host B as 10.1.2.2.
E. Configure the masks on both hosts to be 255.255.255.224.
F. Configure the masks on both hosts to be 255.255.255.240.
Answer: B D
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. For what two reasons has the router loaded its IOS image from the location that is shown? (Choose two)
| Router1> show version Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS ™ 7200 Software (C7200-J-M), Experimental Version 11.3tl997091S:1647S2) [hampton-nitro-baseline 249] Copyright (c) 1986-1997 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Wed 08-0ct-97 06:39 by hampton Image text-base: 0×60008900, data-base: 0x60B98000 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.1(11855) [beta 2], INTERIM SOFTWARE BOOTPLASH: 7200 Software (C7200-BOOT-M), Version 11.1(472), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fcl) Router1 uptime is 23 hours, 33 minutes System restarted by abort at PC 0x6022322C at 10:50:SS PDT Tue Oct 21 1997 System image file is “tftp://112.16.1.129/hampton/nitro/c7200-j-mz” cisco 7206 (NPE150) processor with 57344K/8192K bytes of memory. Configuration register is 0×2102 |
B. Router1 is acting as a TFTP server for other routers.
C. Router1 cannot locate a valid IOS image in flash memory.
D. Router1 defaulted to ROMMON mode and loaded the IOS image from a TFTP server.
E. Cisco routers will first attempt to load a image from TFTP for management purposes.
Answer: A C
Explanation
When powered on, the router first checks its hardware via Power-On Self Test (POST). Then it checks the configuration register to identify where to load the IOS image from. In the output above we learn that the Configuration register value is 0×2102 so the router will try to boot the system image from Flash memory first.
But we also see a line “System image file is “tftp://112.16.1.129/hampton/nitro/c7200-j-mz”. Please notice that this line tells us the image file that the device last started. In this case it is from a TFTP server. Therefore we can deduce that the router could not load the IOS image from the flash and the IOS image has been loaded from TFTP server.
Note:
If the startup-config file is missing or does not specify a location, it will check the following locations for the IOS image:
+ Flash (the default location)
+ TFTP server
+ ROM (used if no other source is found)
Question 8
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two)

A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The last known good router will try to inform you that the destination cannot be reached (with a Destination Unreachable message type) so from that information you can learn how far your packets can travel to and where the problem is.
Question 9
How is an EUI-64 format interface ID created from a 48-bit MAC address?
A. by appending 0xFF to the MAC address.
B. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFFEE.
C. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xFF and appending 0xFF to it.
D. by inserting 0xFFFE between the upper three bytes and the lower three bytes of the MAC address
E. by prefixing the MAC address with 0xF and inserting 0xF after each of its first three bytes.
Answer: D
Explanation
We convert a 48-bit MAC address (IEEE 802) to a 64-bit value by breaking the MAC address into its two 24-bit halves. The first part is the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and the next part is the NIC specific part. Then the 16-bit hex value 0xFFFE is inserted between them to create a 64-bit value.

Just for your information, to obtain an IPv6 interface identifier from EUI-64 address, we have to complement the U/L bit (the seventh bit of the first byte and is used to determine whether the address is universally or locally administered). This means if it is a 1, it is set to 0; and if it is a 0, it is set to 1. In the above example, the U/L bit is 0 (from 00 = 0000 0000). Therefore we have to set this bit to 1 to create an IPv6 interface address.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit:

A network administrator is adding two new hosts to SwitchA. Which three values could be used for the configuration of these hosts? (Choose three)
A. host A IP address: 192.168.1.79
B. host A IP address: 192.168.1.64
C. host A default gateway: 192.168.1.78
D. host B IP address: 192.168.1.128
E. host B default gateway: 192.168.1.129
F. host B IP address: 192.168.1.190
Answer: A C F
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is asked to design a small network with redundancy. The exhibit represents this design, with all hosts configured in the same VLAN. What conclusions can be made about this design?

A. The design will function as intended
B. Spanning-tree will need to be used.
C. The router will not accept the addressing scheme.
D. The connection between switches should be a trunk.
E. The router interfaces must be encapsulated with the 802.1Q protocol.
Answer: C
Explanation
Each interface on a router must be in a different network. If two interfaces are in the same network, the router will not accept it and show error when the administrator assigns it.
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined about the router from the console output?
| 1 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. 65536K bytes of ATA PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 512 bytes) . 8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K). ———-System Configuration Dialog ———- Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: |
B. No configuration file was found in flash.
C. No configuration file was found in the PCMCIA card.
D. Configuration file is normal and will load in 15 seconds.
Answer: A
Explanation
When no startup configuration file is found in NVRAM, the System Configuration Dialog will appear to ask if we want to enter the initial configuration dialog or not.
Question 13
Which command displays CPU utilization?
A. show protocols
B. show process
C. show system
D. show version
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show process” (in fact, the full command is “show processes”) command gives us lots of information about each process but in fact it is not easy to read. Below shows the output of this command (some next pages are omitted)

A more friendly way to check the CPU utilization is the command “show processes cpu history”, in which the total CPU usage on the router over a period of time: one minute, one hour, and 72 hours are clearly shown:

+ The Y-axis of the graph is the CPU utilization.
+ The X-axis of the graph is the increment within the period displayed in the graph
For example, from the last graph (last 72 hours) we learn that the highest CPU utilization within 72 hours is 37% about six hours ago.
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit:

What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose three)
A. Router1 will strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c36.6965.
B. Router1 will strip off the source IP address and replace it with the IP address 192.168.40.1.
C. Router1 will strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c07.4320.
D. Router1 will strip off the destination IP address and replace it with the IP address of 192.168.40.1.
E. Router1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/1.
F. Router1 will forward the data packet out interface FastEthernet0/2.
Answer: A C F
Explanation
The “Age” field in the “show ip arp” command is the age in minutes of the cache entry. A hyphen (-) means the address is local so in this case 192.168.20.1, 192.168.40.1 & 192.168.60.1 are local to this router.
From the “Data Frame”, we learn that a packet is sent to Router1 and Router1 needs to forward it to the Destination IP 192.168.40.5. Therefore this router will:
+ Strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c36.6965 (because the IP address of this interface – 192.168.40.1 is in the same subnet with the Destination IP 192.138.40.5).
+ Strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address 0000.0c07.4320, which is the MAC of Destination host.
+ Forward the data packet out interface FastEthemet0/2 because this interface has the IP address of 192.168.40.1.