Question 1
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:

Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?
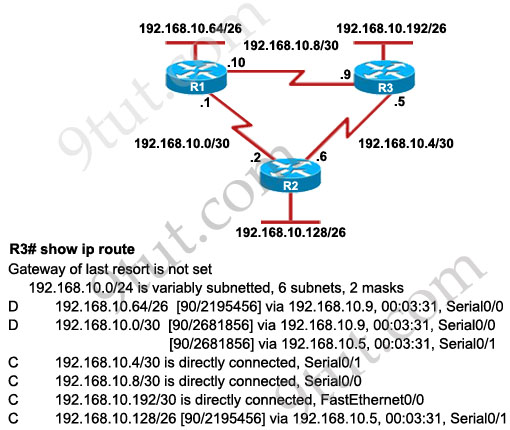
A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1
B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) -> traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit, when running EIGRP what is required for R1 to exchange routing updates with R3?
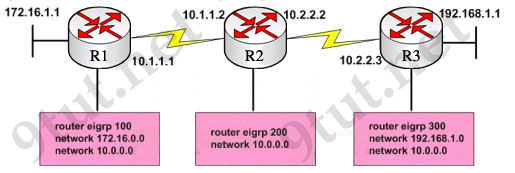
A – AS numbers must be changed to match on all the routers
B – Loopback interfaces must be configured so a DR is elected
C – The no auto-summary command is needed on R1 and R3
D – R2 needs to have two network statements, one for each connected network
Answer: A
Question 4
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a primary route,stored in the routing table
B. a backup route,stored in the routing table
C. a backup route,stored in the topology table
D. a primary route,stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance is less than the Feasible Distance of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but stored in the topology table.
Question 5
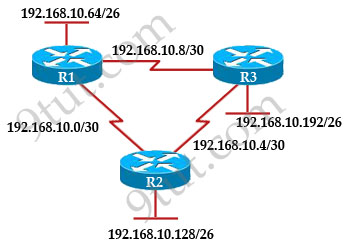
Refer to the exhibit. The company uses EIGRP as the routing protocol. What path will packets take from a host on 192.168.10.192/26 network to a host on the LAN attached to router R1?
R3# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192 168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.10.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
D 192.168.10.0/30 [90/2681856] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
C 192.168.10.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.192/26 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.10.128/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.5,00:03:31, Serial0/1
A. The path of the packets will be R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The path of the packets will be both R3 to R2 to R1 and R3 to R1.
D. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
Host on the LAN attached to router R1 belongs to 192.168.10.64/26 subnet. From the output of the routing table of R3 we learn this network can be reach via 192.168.10.9, which is an IP address in 192.168.10.8/30 network (the network between R1 & R3) -> packets destined for 192.168.10.64 will be routed from R3 -> R1 -> LAN on R1.
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:

Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?

A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1
B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) -> traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit, when running EIGRP what is required for R1 to exchange routing updates with R3?

A – AS numbers must be changed to match on all the routers
B – Loopback interfaces must be configured so a DR is elected
C – The no auto-summary command is needed on R1 and R3
D – R2 needs to have two network statements, one for each connected network
Answer: A
Question 4
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a primary route,stored in the routing table
B. a backup route,stored in the routing table
C. a backup route,stored in the topology table
D. a primary route,stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance is less than the Feasible Distance of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but stored in the topology table.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. The company uses EIGRP as the routing protocol. What path will packets take from a host on 192.168.10.192/26 network to a host on the LAN attached to router R1?

R3# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192 168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.10.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
D 192.168.10.0/30 [90/2681856] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
C 192.168.10.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.192/26 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.10.128/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.5,00:03:31, Serial0/1
A. The path of the packets will be R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The path of the packets will be both R3 to R2 to R1 and R3 to R1.
D. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
Host on the LAN attached to router R1 belongs to 192.168.10.64/26 subnet. From the output of the routing table of R3 we learn this network can be reach via 192.168.10.9, which is an IP address in 192.168.10.8/30 network (the network between R1 & R3) -> packets destined for 192.168.10.64 will be routed from R3 -> R1 -> LAN on R1.