Question 1
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D
Question 2
Which statements describe the routing protocol OSPF? (Choose three)
A. It supports VLSM.
B. It is used to route between autonomous systems.
C. It confines network instability to one area of the network.
D. It increases routing overhead on the network.
E. It allows extensive control of routing updates
F. It is simpler to configure than RIPv2.
Answer: A C E
Explanation
Answer A and C are obviously correct. For answer E, it allows extensive control of routing updates via Link-State Advertisement (LSA). Administrators can filter these LSAs to meet their requirements easily.
Question 3
A network administrator is trying to add a new router into an established OSPF network. The networks attached to the new router do not appear in the routing tables of the other OSPF routers. Given the information in the partial configuration shown below, what configuration error is causing this problem?
A. The process id is configured improperly.
B. The OSPF area is configured improperly.
C. The network wildcard mask is configured improperly.
D. The network number is configured improperly.
E. The AS is configured improperly.
F. The network subnet mask is configured improperly.
Answer: C
Question 4
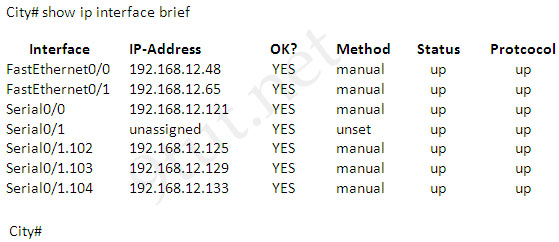
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 5
What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 6 equal-cost paths
Question 6
Which two statements describe the process identifier that is used in the command to configure OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
Router(config)# router ospf 1
A. All OSPF routers in an area must have the same process ID.
B. Only one process number can be used on the same router.
C. Different process identifiers can be used to run multiple OSPF processes
D. The process number can be any number from 1 to 65,535.
E. Hello packets are sent to each neighbor to determine the processor identifier.
Answer: C D
Question 7
Why do large OSPF networks use a hierarchical design? (Choose three)
A. to confine network instability to single areas of the network.
B. to reduce the complexity of router configuration
C. to speed up convergence
D. to lower costs by replacing routers with distribution layer switches
E. to decrease latency by increasing bandwidth
F. to reduce routing overhead
Answer: A C F
Explanation
Hierarchical design of OSPF (basically means that you can separate the larger internetwork into smaller internetworks called areas) helps us create a network with all features listed above (decrease routing overhead, speed up convergence, confine network instability to single areas of the network).
Question 8
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (choose two)
A. Router(config)#router ospf 1
B. Router(config)#router ospf 0
C. Router(config)#router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
E. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
F. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: A D
Explanation
In the router ospf command, the ranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> A is correct but B is not correct.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this RouterD?
RouterD# show ip interface brief

A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.316
Answer: C
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 10
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 120
B. 100
C. 90
D. 110
Answer: D
Question 11
Why R1 can’t establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3 according to the following graphic? (Choose two)
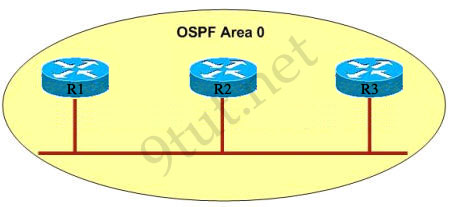
A – Configure EIGRP on these routers with a lower administrative distance
B – All routers should be configured for backbone Area 1
C – R1 and R3 have been configured in different areas
D – The hello and dead interval timers are not configured the same values on R1 and R3
Answer: C D
Explanation
A is not correct because configure EIGRP on these routers (with a lower administrative distance) will force these routers to run EIGRP, not OSPF.
B is not correct because the backbone area of OSPF is always Area 0.
C and D are correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
- Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
Question 12
Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
B. Bandwidth
C. Bandwidth and MTU
D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Answer: B
Explanation
The well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost is
Cost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
Question 13
A network administrator is troubleshooting the OSPF configuration of routers R1 and R2. The routers cannot establish an adjacency relationship on their common Ethernet link. The graphic shows the output of the show ip ospf interface e0 command for routers R1 and R2. Based on the information in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?
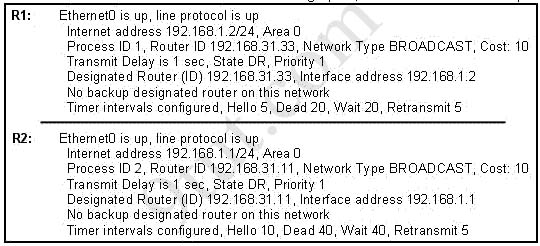
A. The OSPF area is not configured properly.
B. The priority on R1 should be set higher.
C. The cost on R1 should be set higher.
D. The hello and dead timers are not configured properly.
E. A backup designated router needs to be added to the network.
F. The OSPF process ID numbers must match.
Answer: D
Explanation
D is correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
- Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
In this case Ethernet0 of R1 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 5 and 20 while R2 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 10 and 40 -> R1 and R2 cannot form OSPF neighbor relationship.
Question 14
What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C
Question 15
Which command is used to display the collection of OSPF link states?
A. show ip ospf link-state
B. show ip ospf lsa database
C. show ip ospf neighbors
D. show ip ospf database
Answer: D
Question 16
When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?
A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.
C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Answer: B
Explanation
To form an adjacency (become neighbor), router A & B must have the same Hello interval, Dead interval and AREA number.
Question 17
Which is true about OSPF router-id? (Choose two)
A. It is used for type 1 router LSA
B. Highest IP address of the loopback is used
C. router-id needs to be matched on ospf neighbors
D. router-id is 16 bit
Answer: A B
Explanation
OSPF LSA Type 1 (or Router LSA) is generated by all routers in an area to describe their directly attached links. An example below shows this type of LSA:

As you can see, the LSA Type 1 uses the router ID to advertise itself (1.1.1.1 or 2.2.2.2).
The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D
Question 2
Which statements describe the routing protocol OSPF? (Choose three)
A. It supports VLSM.
B. It is used to route between autonomous systems.
C. It confines network instability to one area of the network.
D. It increases routing overhead on the network.
E. It allows extensive control of routing updates
F. It is simpler to configure than RIPv2.
Answer: A C E
Explanation
Answer A and C are obviously correct. For answer E, it allows extensive control of routing updates via Link-State Advertisement (LSA). Administrators can filter these LSAs to meet their requirements easily.
Question 3
A network administrator is trying to add a new router into an established OSPF network. The networks attached to the new router do not appear in the routing tables of the other OSPF routers. Given the information in the partial configuration shown below, what configuration error is causing this problem?
| Router(config)# router ospf 1 Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0 |
B. The OSPF area is configured improperly.
C. The network wildcard mask is configured improperly.
D. The network number is configured improperly.
E. The AS is configured improperly.
F. The network subnet mask is configured improperly.
Answer: C
Question 4

A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 5
What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 6 equal-cost paths
Question 6
Which two statements describe the process identifier that is used in the command to configure OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
Router(config)# router ospf 1
A. All OSPF routers in an area must have the same process ID.
B. Only one process number can be used on the same router.
C. Different process identifiers can be used to run multiple OSPF processes
D. The process number can be any number from 1 to 65,535.
E. Hello packets are sent to each neighbor to determine the processor identifier.
Answer: C D
Question 7
Why do large OSPF networks use a hierarchical design? (Choose three)
A. to confine network instability to single areas of the network.
B. to reduce the complexity of router configuration
C. to speed up convergence
D. to lower costs by replacing routers with distribution layer switches
E. to decrease latency by increasing bandwidth
F. to reduce routing overhead
Answer: A C F
Explanation
Hierarchical design of OSPF (basically means that you can separate the larger internetwork into smaller internetworks called areas) helps us create a network with all features listed above (decrease routing overhead, speed up convergence, confine network instability to single areas of the network).
Question 8
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (choose two)
A. Router(config)#router ospf 1
B. Router(config)#router ospf 0
C. Router(config)#router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
E. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
F. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: A D
Explanation
In the router ospf command, the ranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> A is correct but B is not correct.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this RouterD?
RouterD# show ip interface brief

A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.316
Answer: C
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 10
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 120
B. 100
C. 90
D. 110
Answer: D
Question 11
Why R1 can’t establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3 according to the following graphic? (Choose two)

A – Configure EIGRP on these routers with a lower administrative distance
B – All routers should be configured for backbone Area 1
C – R1 and R3 have been configured in different areas
D – The hello and dead interval timers are not configured the same values on R1 and R3
Answer: C D
Explanation
A is not correct because configure EIGRP on these routers (with a lower administrative distance) will force these routers to run EIGRP, not OSPF.
B is not correct because the backbone area of OSPF is always Area 0.
C and D are correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
- Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
Question 12
Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
B. Bandwidth
C. Bandwidth and MTU
D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Answer: B
Explanation
The well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost is
Cost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
Question 13
A network administrator is troubleshooting the OSPF configuration of routers R1 and R2. The routers cannot establish an adjacency relationship on their common Ethernet link. The graphic shows the output of the show ip ospf interface e0 command for routers R1 and R2. Based on the information in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?

A. The OSPF area is not configured properly.
B. The priority on R1 should be set higher.
C. The cost on R1 should be set higher.
D. The hello and dead timers are not configured properly.
E. A backup designated router needs to be added to the network.
F. The OSPF process ID numbers must match.
Answer: D
Explanation
D is correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
- Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
In this case Ethernet0 of R1 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 5 and 20 while R2 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 10 and 40 -> R1 and R2 cannot form OSPF neighbor relationship.
Question 14
What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C
Question 15
Which command is used to display the collection of OSPF link states?
A. show ip ospf link-state
B. show ip ospf lsa database
C. show ip ospf neighbors
D. show ip ospf database
Answer: D
Question 16
When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?

A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.
C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Answer: B
Explanation
To form an adjacency (become neighbor), router A & B must have the same Hello interval, Dead interval and AREA number.
Question 17
Which is true about OSPF router-id? (Choose two)
A. It is used for type 1 router LSA
B. Highest IP address of the loopback is used
C. router-id needs to be matched on ospf neighbors
D. router-id is 16 bit
Answer: A B
Explanation
OSPF LSA Type 1 (or Router LSA) is generated by all routers in an area to describe their directly attached links. An example below shows this type of LSA:

As you can see, the LSA Type 1 uses the router ID to advertise itself (1.1.1.1 or 2.2.2.2).
The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned