Question 1
A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E
Question 2
Refer to the graphic.
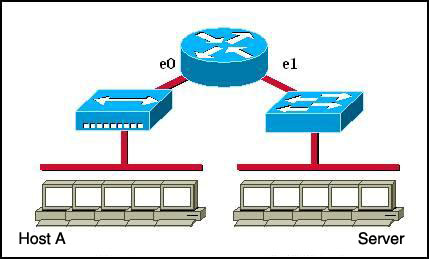
Host A is communicating with the server. What will be the source MAC address of the frames received by Host A from the server?
A. the MAC address of router interface e0
B. the MAC address of router interface e1
C. the MAC address of the server network interface
D. the MAC address of host A
Answer: A
Question 3
A router has learned three possible routes that could be used to reach a destination network. One route is from EIGRP and has a composite metric of 20514560. Another route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The last is from RIPv2 and has a metric of 4. Which route or routes will the router install in the routing table?
A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B
Explanation
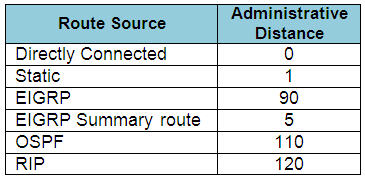
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing protocols are listed below:
Question 4
A router has two FastEthernet interfaces and needs to connect to four vlans in the local network. How can you accomplish this task, using the fewest physical interfaces and without decreasing network performance?
A. Add two more FastEthernet interfaces.
B. Add a second router to handle the vlan traffic.
C. Use a hub to connect the four vlans with a FastEthernet interface on router.
D. Implement a router-on-a-stick configuration.
Answer: D
Question 5
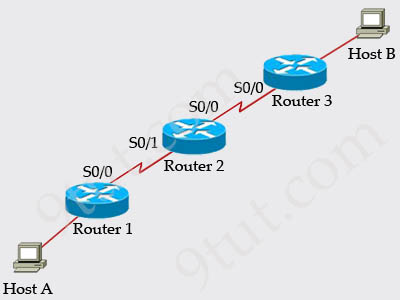
Refer to the exhibit, Host A pings interface S0/0 on router 3, what is the TTL value for that ping?
A. 253
B. 252
C. 255
D. 254
Answer: A
Explanation
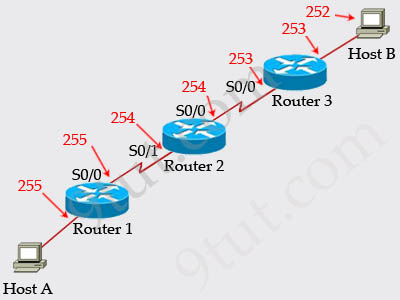
From the CCNA ICND2 Exam book: “Routers decrement the TTL by 1 every time they forward a packet; if a router decrements the TTL to 0, it throws away the packet. This prevents packets from rotating forever.” I want to make it clear that before the router forwards a packet, the TTL is still remain the same. For example in the topology above, pings to S0/1 and S0/0 of Router 2 have the same TTL.
The picture below shows TTL values for each interface of each router and for Host B. Notice that Host A initializes ICMP packet with a TTL of 255:
Question 6
If IP routing is enabled, which two commands set the gateway of last resort to the default gateway? (Choose two)
A. ip default-gateway 0.0.0.0
B. ip route 172.16.2.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
C. ip default-network 0.0.0.0
D. ip default-route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
Answer: C E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping Host2 from Host1 and receives the results that are shown. What is a possible problem?
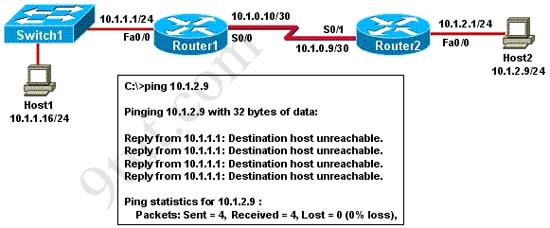
A. The link between Host1 and Switch1 is down.
B. TCP/IP is not functioning on Host1
C. The link between Router1 and Router2 is down.
D. The default gateway on Host1 is incorrect.
E. Interface Fa0/0 on Router1 is shutdown.
F. The link between Switch1 and Router1 is down.
Answer: C
Explanation
In this question, Host1 wants to ping Host2 but it receives a reply from the interface Fa0/0 of Router1 (10.1.1.1/24) that the “destination host unreachable”.
If the link between Host1 and Switch1 is down or the link between Switch1 and Router1 is down then Host1 can not receive this reply -> A and F are not correct.
Host1 can receive a reply from 10.1.1.1 -> the TCP/IP is working properly -> B is not correct.
For answer D, if the default gateway was not configured correctly on Host1 (in this case the default gateway should be 10.1.1.1/24) then 10.1.1.1 can not receive the ping packets from Host1 and can not reply for Host1 that the destination is unreachable -> D is not correct.
Interface Fa0/0 on Router1 replies for the ping packets from Host1 so it is up -> E is not correct. If the interface Fa0/0 on Router is shutdown then we will receive a message of “Request timed out”, not “Destination host unreachable”.
Answer C is correct because we can get a reply from the interface Fa0/0 of Router1 so the link between Host1 and Router1 should be fine -> the problem lies at the other side of Router1. But if the link between Router2 and Host2 is down then we will receive a reply from interface S0/1 of Router2 that the “destination host unreachable”. Therefore the problem can just be the link between Router1 and Router2.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator requires easy configuration options and minimal routing protocol traffic. Which two options provide adequate routing table information for traffic that passes between the two routers and satisfy the requests of the network administrator? (choose two)
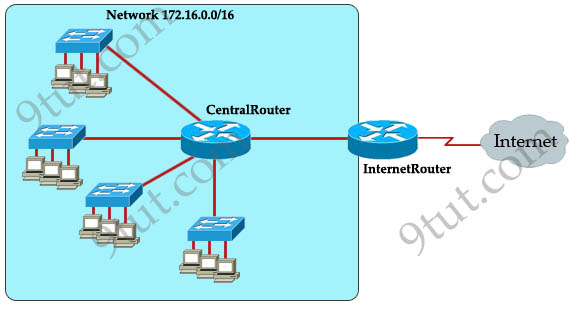
A. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise summarized routers to CentralRouter.
B. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouter to advertise summarized routers to InternetRouter.
C. a static route on InternetRouter to direct traffic that is destined for 172.16.0.0/16 to CentralRouter.
D. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise all routes to CentralRouter.
E. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouer to advertise all routes to InternetRouter
F. a static, default route on CentralRouter that directs traffic to InternetRouter.
Answer: C F
Question 9
Refer to the graphic. A static route to the 10.5.6.0/24 network is to be configured on the HFD router. Which commands will accomplish this? (Choose two)
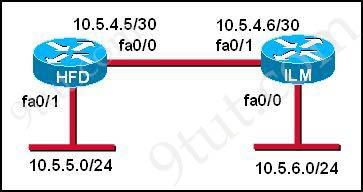
A. HFD (config) #ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 fa0/0
B. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 10.5.4.6
C. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0
D. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 10.5.4.6
E. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 0.0.0.255 10.5.6.0
F. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 255.255.255.0 10.5.6.0
Answer: C D
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
In the statement “ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0″:
+ 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0: the destination network
+ fa0/0: the exit-interface
Question 10
Users on the 172.17.22.0 network cannot reach the server located on the 172.31.5.0 network. The network administrator connected to router Coffee via the console port, issued the show ip route command. Based on the output of the show ip route command and the topology shown in the graphic, what is the cause of the failure?
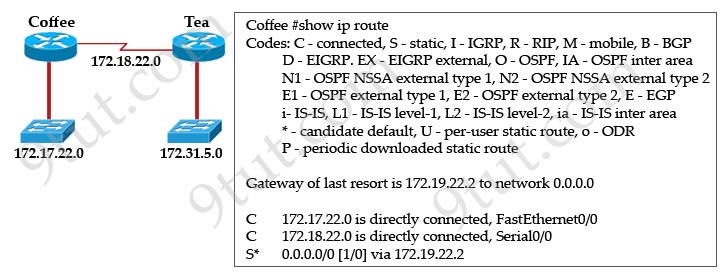
A. The network has not fully converged.
B. IP routing is not enabled.
C. A static route is configured incorrectly.
D. The FastEthernet interface on Coffee is disabled.
E. The neighbor relationship table is not correctly updated.
F. The routing table on Coffee has not updated.
Answer: C
Explanation
There are no dynamic routing protocols running on Coffee router, only a default route is configured to route all traffic to 172.19.22.2 but we don’t know about this network. The correct IP address should be the IP address on the interface of Tea router which is connected to Coffee router (maybe 172.18.22.2).
Question 11
The speed of all serial links is E1 and the speed of the all other links is 100Mb/s. A static route will be established on the Manchester router to direct traffic toward to the internet over the most direct path available. What configuration of the Manchester router will establish a route toward to the internet for traffic from workstation on the Manchester LAN?
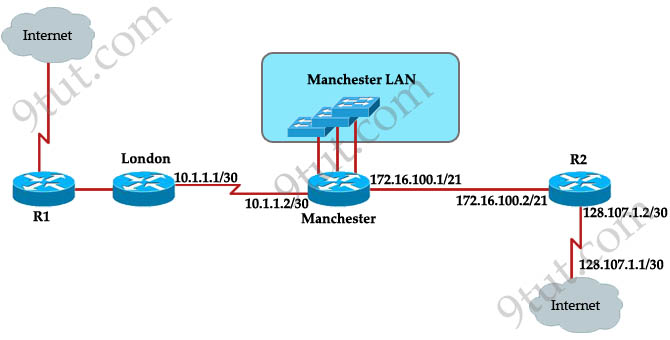
A. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
B. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.1.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.107.1.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.00.0:0:[IMG]resource://skype_ff_extension-at-jetpack/skype_ff_extension/data/call_skype_logo.png[/IMG]0 172.16.100.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 172.16.100.2
F. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2
Answer: F
Explanation
Maybe “the most direct path available” here means via R2 because it is directly connected with the Internet while the London path needs to go through R1. So we need a command to send traffic to R2 and the correct command is “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2″.
Question 12
Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (choose two)
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29″ will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3 -> C is correct.
Question 14
Which destination addresses will be used by Host A to send data to Host C? (Choose two)
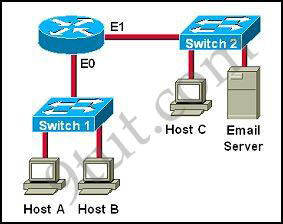
A. the IP address of Switch 1
B. the MAC address of Switch 1
C. the IP address of Host C
D. the MAC address of Host C
E. the IP address of the router’s E0 interface
F. the MAC address of the router’s E0 interface
Answer: C F
Explanation
While transferring data through many different networks, the source and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case Host A will use the IP address of Host C and the MAC address of E0 interface to send data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC address with it own E1 interface’s MAC address and replaces the destination MAC address with Host C’s MAC address before sending to Host C -> C and F are correct.
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator must establish a route by which London workstations can forward traffic to the Manchester workstations. What is the simplest way to accomplish this?
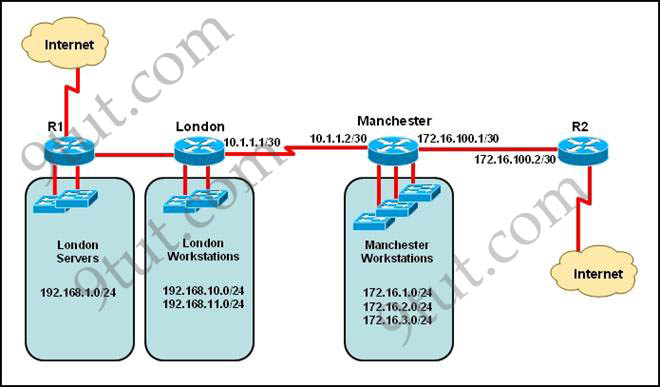
A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise all routes to Manchester.
B. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise summarized routes to Manchester.
C. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on Manchester to advertise a default route to the London router.
D. Configure a static default route on London with a next hop of 10.1.1.1.
E. Configure a static route on London to direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 to 10.1.1.2.
F. Configure Manchester to advertise a static default route to London.
Answer: E
Question 16
Which parameter can be tuned to affect the selection of a static route as a backup when a dynamic protocol is also being used?
A. link bandwidth
B. hop count
C. link cost
D. administrative distance
E. link delay
Answer: D
Question 17
Refer to the exhibit:
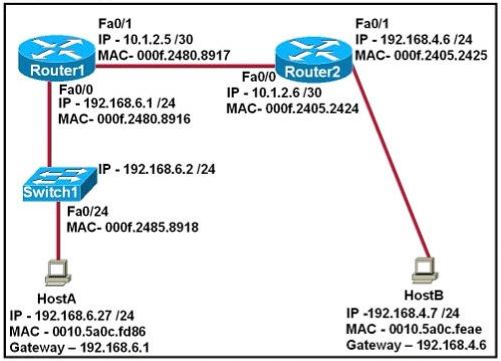
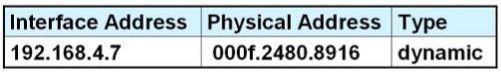
After HostA pings HostB, which entry will be in the ARP cache of HostA to support this transmission?
A.
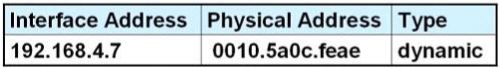
B.
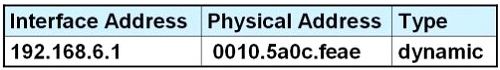
C.
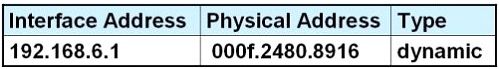
D.
E.
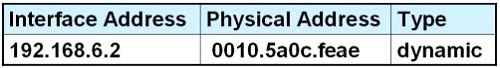
F.

Answer: D
Explanation
Host A knows host B is in another network so it will send the pings to its default gateway 192.168.6.1. Host A sends a broadcast frame asking the MAC address of 192.168.6.1. These information (IP and MAC address of the default gateway) is saved in its ARP cache for later use.
A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E
Question 2
Refer to the graphic.

Host A is communicating with the server. What will be the source MAC address of the frames received by Host A from the server?
A. the MAC address of router interface e0
B. the MAC address of router interface e1
C. the MAC address of the server network interface
D. the MAC address of host A
Answer: A
Question 3
A router has learned three possible routes that could be used to reach a destination network. One route is from EIGRP and has a composite metric of 20514560. Another route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The last is from RIPv2 and has a metric of 4. Which route or routes will the router install in the routing table?
A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B
Explanation
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing protocols are listed below:

Question 4
A router has two FastEthernet interfaces and needs to connect to four vlans in the local network. How can you accomplish this task, using the fewest physical interfaces and without decreasing network performance?
A. Add two more FastEthernet interfaces.
B. Add a second router to handle the vlan traffic.
C. Use a hub to connect the four vlans with a FastEthernet interface on router.
D. Implement a router-on-a-stick configuration.
Answer: D
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit, Host A pings interface S0/0 on router 3, what is the TTL value for that ping?

A. 253
B. 252
C. 255
D. 254
Answer: A
Explanation
From the CCNA ICND2 Exam book: “Routers decrement the TTL by 1 every time they forward a packet; if a router decrements the TTL to 0, it throws away the packet. This prevents packets from rotating forever.” I want to make it clear that before the router forwards a packet, the TTL is still remain the same. For example in the topology above, pings to S0/1 and S0/0 of Router 2 have the same TTL.
The picture below shows TTL values for each interface of each router and for Host B. Notice that Host A initializes ICMP packet with a TTL of 255:

Question 6
If IP routing is enabled, which two commands set the gateway of last resort to the default gateway? (Choose two)
A. ip default-gateway 0.0.0.0
B. ip route 172.16.2.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
C. ip default-network 0.0.0.0
D. ip default-route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
Answer: C E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping Host2 from Host1 and receives the results that are shown. What is a possible problem?

A. The link between Host1 and Switch1 is down.
B. TCP/IP is not functioning on Host1
C. The link between Router1 and Router2 is down.
D. The default gateway on Host1 is incorrect.
E. Interface Fa0/0 on Router1 is shutdown.
F. The link between Switch1 and Router1 is down.
Answer: C
Explanation
In this question, Host1 wants to ping Host2 but it receives a reply from the interface Fa0/0 of Router1 (10.1.1.1/24) that the “destination host unreachable”.
If the link between Host1 and Switch1 is down or the link between Switch1 and Router1 is down then Host1 can not receive this reply -> A and F are not correct.
Host1 can receive a reply from 10.1.1.1 -> the TCP/IP is working properly -> B is not correct.
For answer D, if the default gateway was not configured correctly on Host1 (in this case the default gateway should be 10.1.1.1/24) then 10.1.1.1 can not receive the ping packets from Host1 and can not reply for Host1 that the destination is unreachable -> D is not correct.
Interface Fa0/0 on Router1 replies for the ping packets from Host1 so it is up -> E is not correct. If the interface Fa0/0 on Router is shutdown then we will receive a message of “Request timed out”, not “Destination host unreachable”.
Answer C is correct because we can get a reply from the interface Fa0/0 of Router1 so the link between Host1 and Router1 should be fine -> the problem lies at the other side of Router1. But if the link between Router2 and Host2 is down then we will receive a reply from interface S0/1 of Router2 that the “destination host unreachable”. Therefore the problem can just be the link between Router1 and Router2.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator requires easy configuration options and minimal routing protocol traffic. Which two options provide adequate routing table information for traffic that passes between the two routers and satisfy the requests of the network administrator? (choose two)

A. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise summarized routers to CentralRouter.
B. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouter to advertise summarized routers to InternetRouter.
C. a static route on InternetRouter to direct traffic that is destined for 172.16.0.0/16 to CentralRouter.
D. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise all routes to CentralRouter.
E. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouer to advertise all routes to InternetRouter
F. a static, default route on CentralRouter that directs traffic to InternetRouter.
Answer: C F
Question 9
Refer to the graphic. A static route to the 10.5.6.0/24 network is to be configured on the HFD router. Which commands will accomplish this? (Choose two)

A. HFD (config) #ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 fa0/0
B. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 10.5.4.6
C. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0
D. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 10.5.4.6
E. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 0.0.0.255 10.5.6.0
F. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 255.255.255.0 10.5.6.0
Answer: C D
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
In the statement “ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0″:
+ 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0: the destination network
+ fa0/0: the exit-interface
Question 10
Users on the 172.17.22.0 network cannot reach the server located on the 172.31.5.0 network. The network administrator connected to router Coffee via the console port, issued the show ip route command. Based on the output of the show ip route command and the topology shown in the graphic, what is the cause of the failure?

A. The network has not fully converged.
B. IP routing is not enabled.
C. A static route is configured incorrectly.
D. The FastEthernet interface on Coffee is disabled.
E. The neighbor relationship table is not correctly updated.
F. The routing table on Coffee has not updated.
Answer: C
Explanation
There are no dynamic routing protocols running on Coffee router, only a default route is configured to route all traffic to 172.19.22.2 but we don’t know about this network. The correct IP address should be the IP address on the interface of Tea router which is connected to Coffee router (maybe 172.18.22.2).
Question 11
The speed of all serial links is E1 and the speed of the all other links is 100Mb/s. A static route will be established on the Manchester router to direct traffic toward to the internet over the most direct path available. What configuration of the Manchester router will establish a route toward to the internet for traffic from workstation on the Manchester LAN?

A. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
B. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.1.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.107.1.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.00.0:0:[IMG]resource://skype_ff_extension-at-jetpack/skype_ff_extension/data/call_skype_logo.png[/IMG]0 172.16.100.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 172.16.100.2
F. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2
Answer: F
Explanation
Maybe “the most direct path available” here means via R2 because it is directly connected with the Internet while the London path needs to go through R1. So we need a command to send traffic to R2 and the correct command is “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2″.
Question 12
Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (choose two)
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
| Network | Interface | Next-hop |
| 10.1.1.0/24 | e0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.2.0/24 | e1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.3.0/25 | s0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.4.0/24 | s1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.5.0/24 | e0 | 10.1.1.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/28 | e1 | 10.1.2.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/29 | s0 | 10.1.3.3 |
| 10.1.5.64/27 | s1 | 10.1.4.4 |
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29″ will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3 -> C is correct.
Question 14
Which destination addresses will be used by Host A to send data to Host C? (Choose two)

A. the IP address of Switch 1
B. the MAC address of Switch 1
C. the IP address of Host C
D. the MAC address of Host C
E. the IP address of the router’s E0 interface
F. the MAC address of the router’s E0 interface
Answer: C F
Explanation
While transferring data through many different networks, the source and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case Host A will use the IP address of Host C and the MAC address of E0 interface to send data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC address with it own E1 interface’s MAC address and replaces the destination MAC address with Host C’s MAC address before sending to Host C -> C and F are correct.
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator must establish a route by which London workstations can forward traffic to the Manchester workstations. What is the simplest way to accomplish this?

A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise all routes to Manchester.
B. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise summarized routes to Manchester.
C. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on Manchester to advertise a default route to the London router.
D. Configure a static default route on London with a next hop of 10.1.1.1.
E. Configure a static route on London to direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 to 10.1.1.2.
F. Configure Manchester to advertise a static default route to London.
Answer: E
Question 16
Which parameter can be tuned to affect the selection of a static route as a backup when a dynamic protocol is also being used?
A. link bandwidth
B. hop count
C. link cost
D. administrative distance
E. link delay
Answer: D
Question 17
Refer to the exhibit:

After HostA pings HostB, which entry will be in the ARP cache of HostA to support this transmission?
A.

B.

C.

D.

E.

F.

Answer: D
Explanation
Host A knows host B is in another network so it will send the pings to its default gateway 192.168.6.1. Host A sends a broadcast frame asking the MAC address of 192.168.6.1. These information (IP and MAC address of the default gateway) is saved in its ARP cache for later use.