OSPF process ID giống nhau ở Customer A và khác nhau ở Customer B
Mô tả:
Mục tiêu của bài này là hiểu được cách OSPF process ID tham gia quyết định loại tuyến thấy được ở phía router biên của khách hàng chạy OSPF như thế nào.
- Mạng Customer A – Customer A có CE2-A và CE2-A trong cùng VPN-A và cùng OSPF domain. PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1 có OSPF process ID 101 được cấu hình cho VRF CustomerA trên PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1.
- Mạng Customer B – Customer B có CE1-B và CE2-B trong VPN-B. PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1 có OSPF process ID là 201 và 202 cho hai CustomerB VRF.
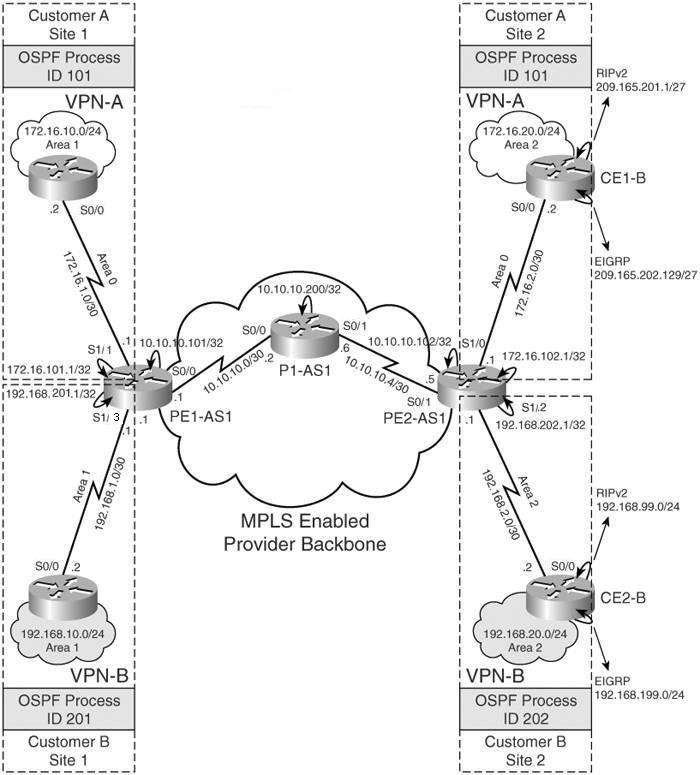
Thực hiện:
Trước khi cấu hình, chắc chắn rằng mạng nhà cung cấp cung cấp các dịch vụ MPLS VPN cho các Site CustomerA và B. Cấu hình địa chỉ IP và xác định các VRF trên các router PE.
Ví dụ: Cấu hình VRF và các thuộc tính của nó trên router PE1-AS1 định tuyến OSPF PE-CE cho VRF CustomerA:
PE1-AS1(config)#ip vrf CustomerAPE1-AS1(config-vrf)#rd 1:100PE1-AS1(config-vrf)#route-target both 1:100PE1-AS1(config)#interface Serial1/0PE1-AS1(config-if)#description connected to CE1-APE1-AS1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding CustomerA
PE1-AS1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
Các bước cấu hình OSPF PE-CE trên các router PE:
- Cho phép dịnh tuyến trên VRF OSPF
Cho phép định tuyến trên VRF OSPF cho CustomerA trên PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1:
PE1-AS1(config)#router ospf 101 vrf CustomerAPE1-AS1(config-router)#router-id 172.16.101.1
PE1-AS1(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
PE2-AS1(config)#router ospf 101 vrf CustomerAPE2-AS1(config-router)#router-id 172.16.102.1
PE2-AS1(conig-router)#network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- Redistribute các tuyến OSPF vào BGP
Các tuyến OSPF nhận được từ các router CE được redistribute vào MP-iBGP. Chỉ redistribute những tuyến nội (internal routes).
PE1-AS1(config)#router bgp 1PE1-AS1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerAPE1-AS1(config-router-af)#redistribute ospf 101 vrf CustomerA match internal external 1 external 2PE2-AS1(config)#router bgp 1PE2-AS1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerAPE2-AS1(config-router-af)#redistribute ospf 101 vrf CustmerA match internal external 1 external 2
- Redistribute MP-iBGP vào OSPF
Thực hiện redistribute các tuyến BGP VPNv4 vào lại OSPF trên các router PE.
PE1-AS1(config)#router ospf 100 vrf CustomerAPE1-AS1(config-router)#redistribute bgp 1 subnetsPE2-AS1(config)#router ospf 100 vrf CustomerAPE2-AS1(config-router)#redistribute bgp 1 subnets
Cấu hình tương tự với định tuyến VRF OSPF cho CustomerB
Cấu hình
Router P1-AS1
!
hostname P1-AS1
!
ip subnet-zero
!
ip cef
mpls ldp logging neighbor-changes
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.10.200 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to PE1-AS1
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
clockrate 64000
!
interface Serial0/1
description Connected to PE2-AS1
ip address 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
clockrate 64000
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
!
ip classless
!
call rsvp-sync
!
end
Router PE1-AS1
!
hostname PE1-AS1
!
ip subnet-zero
!
ip vrf CustomerA
rd 1:100
route-target export 1:100
route-target import 1:100
!
ip vrf CustomerB
rd 1:200
route-target export 1:200
route-target import 1:200
!
ip cef
mpls ldp logging neighbor-changes
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.10.101 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback101
description OSPF Router ID for VRF CustomerA
ip vrf forwarding CustomerA
ip address 172.16.101.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback201
description OSPF Router ID for VRF CustomerB
ip vrf forwarding CustomerB
ip address 192.168.201.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to P1-AS1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!
interface Serial1/1
description Connected to CE1-A
ip vrf forwarding CustomerA
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
clockrate 64000
!
interface Serial1/3
description Connected to CE1-B
ip vrf forwarding CustomerB
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252
!
router ospf 101 vrf CustomerA
router-id 172.16.101.1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute bgp 1 subnets
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
!
router ospf 201 vrf CustomerB
router-id 192.168.201.1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute bgp 1 subnets
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 1
!
router ospf 1
router-id 10.10.10.101
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.10.10.102 remote-as 1
neighbor 10.10.10.102 update-source Loopback0
no auto-summary
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 10.10.10.102 activate
neighbor 10.10.10.102 send-community extended
no auto-summary
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerB
redistribute ospf 201 match internal external 1 external 2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerA
redistribute ospf 101 match internal external 1 external 2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ip http server
ip classless
!
end
Router PE2-AS1
!
hostname PE2-AS1
!
ip subnet-zero
!
ip vrf CustomerA
rd 1:100
route-target export 1:100
route-target import 1:100
!
ip vrf CustomerB
rd 1:200
route-target export 1:200
route-target import 1:200
!
ip cef
mpls ldp logging neighbor-changes
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.10.102 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback101
description OSPF Router ID for VRF CustomerA
ip vrf forwarding CustomerA
ip address 172.16.102.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback202
description OSPF Router ID for VRF CustomerB
ip vrf forwarding CustomerB
ip address 192.168.202.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0/1
description Connected to P1-AS1
ip address 10.10.10.5 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!
interface Serial1/0
description Connected to CE2-A
ip vrf forwarding CustomerA
ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.252
clockrate 64000
!
interface Serial1/2
description Connected to CE2-B
ip vrf forwarding CustomerB
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.252
clockrate 64000
!
router ospf 101 vrf CustomerA
router-id 172.16.102.1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute bgp 1 subnets
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
!
router ospf 202 vrf CustomerB
router-id 192.168.202.1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute bgp 1 subnets
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 2
!
router ospf 1
router-id 10.10.10.102
log-adjacency-changes
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.10.10.101 remote-as 1
neighbor 10.10.10.101 update-source Loopback0
no auto-summary
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 10.10.10.101 activate
neighbor 10.10.10.101 send-community extended
no auto-summary
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerB
redistribute ospf 202 match internal external 1 external 2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf CustomerA
redistribute ospf 101 match internal external 1 external 2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ip http server
ip classless
!
end
Router CE1-A
!
hostname CE1-A
!
ip subnet-zero
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description VPN-A Site 1 network
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
half-duplex
no keepalive
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to PE1-AS1
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.252
no fair-queue
!
router ospf 101
log-adjacency-changes
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
!
ip classless
!
end
Router CE2-A
!
hostname CE2-A
!
ip subnet-zero
!
interface Loopback0
description RIPv2 network
ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
!
interface Loopback1
description EIGRP network
ip address 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.224
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description VPN-A Site 2 network
ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0
half-duplex
no keepalive
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to PE2-AS1
ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.252
no fair-queue
!
router eigrp 1
network 209.165.202.0
no auto-summary
!
router ospf 101
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute eigrp 1 subnets
redistribute rip metric-type 1 subnets
network 172.16.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 172.16.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
!
router rip
version 2
redistribute ospf 101 match internal external 1 external 2
network 209.165.201.0
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
!
end
Router CE1-B
!
hostname CE1-B
!
ip subnet-zero
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description VPN-B Site 1 network
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
no keepalive
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to PE1-AS1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252
clockrate 64000
no fair-queue
!
router ospf 201
log-adjacency-changes
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
!
ip classless
!
end
Router CE2-B
!
hostname CE2-B
!
ip subnet-zero
!
interface Loopback0
description RIPv2 network
ip address 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback1
description EIGRP network
ip address 192.168.199.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description VPN-B site 2 network
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
half-duplex
no keepalive
!
interface Serial0/0
description Connected to PE2-AS1
ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.252
no fair-queue
!
router eigrp 1
redistribute ospf 202 metric 1500 1 255 1 1500 match internal external 1 external 2
network 192.168.199.0
no auto-summary
!
router ospf 202
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute eigrp 1 subnets
redistribute rip metric-type 1 subnets
network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
!
router rip
version 2
redistribute ospf 202 metric 1 match internal external 1 external 2
network 192.168.99.0
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
!
end
Kiểm tra:
Các bước kiểm tra định tuyến OSPF PE-CE như sau:
- Kiểm tra quan hệ neighbor và adjacency giữa các router PE và các router biên CE:
PE1-AS1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.10.10.200 0 FULL/ - 00:00:37 10.10.10.2 Serial0/0
192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:35 192.168.1.2 Serial1/3
172.16.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:30 172.16.1.2 Serial1/1
PE2-AS1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.10.10.200 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 10.10.10.6 Serial0/1
192.168.199.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:38 192.168.2.2 Serial1/2
209.165.202.129 0 FULL/ - 00:00:35 172.16.2.2 Serial1/0
- Kiểm tra việc quảng bá tuyến cho CustomerA
Bảng định tuyến VRF cho CustomerA nhận được các tuyến do CE2-A quảng bá tới.
PE2-AS1#show ip route vrf CustomerA ospf 101
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 3 masks
O IA 172.16.20.0/24 [110/791] via 172.16.2.2, 00:44:34, Serial1/0
209.165.201.0/27 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E1 209.165.201.0 [110/801] via 172.16.2.2, 00:44:34, Serial1/0
209.165.202.0/27 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 209.165.202.128 [110/20] via 172.16.2.2, 00:44:34, Serial1/0
Các tuyến OSPF này được redistribute vào MP-iBGP và các metric của tuyến OSPF được sao chép vào các thuộc tính mở rộng của BGP như các BGP MED. Sau đó các tuyến này được quảng bá tới PE1-AS1 bằng MP-iBGP session.
PE2-AS1#show ip bgp vpn vrf CustomerA
BGP table version is 33, local router ID is 10.10.10.102
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:100 (default for vrf CustomerA)
*>i172.16.1.0/30 10.10.10.101 0 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.2.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
*>i172.16.10.0/24 10.10.10.101 791 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.20.0/24 172.16.2.2 791 32768 ?
*>i172.16.101.1/32 10.10.10.101 0 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.102.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
*> 209.165.201.0/27 172.16.2.2 801 32768 ?
*> 209.165.202.128/27
172.16.2.2 20 32768 ?
PE2-AS1#show ip bgp vpnv4 all 172.16.20.0
BGP routing table entry for 1:100:172.16.20.0/24, version 13
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table CustomerA)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.10.10.101
Local
172.16.2.2 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.10.102)
Origin incomplete, metric 791, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:1:100 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.101 OSPF RT:0.0.0.0:3:0 OSPF ROUTER ID:172.16.102.1:0
PE2-AS1#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf CustomerA
BGP table version is 33, local router ID is 10.10.10.102
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:100 (default for vrf CustomerA)
*>i172.16.1.0/30 10.10.10.101 0 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.2.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
*>i172.16.10.0/24 10.10.10.101 791 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.20.0/24 172.16.2.2 791 32768 ?
*>i172.16.101.1/32 10.10.10.101 0 100 0 ?
*> 172.16.102.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
*> 209.165.201.0/27 172.16.2.2 801 32768 ?
*> 209.165.202.128/27
172.16.2.2 20 32768 ?
CE1-A#show ip route ospf
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 3 masks
O IA 172.16.20.0/24 [110/855] via 172.16.1.1, 00:41:36, Serial0/0
O IA 172.16.2.0/30 [110/65] via 172.16.1.1, 00:41:36, Serial0/0
O 172.16.101.1/32 [110/65] via 172.16.1.1, 01:05:21, Serial0/0
O IA 172.16.102.1/32 [110/65] via 172.16.1.1, 00:41:36, Serial0/0
209.165.201.0/27 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E1 209.165.201.0 [110/865] via 172.16.1.1, 00:41:36, Serial0/0
209.165.202.0/27 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 209.165.202.128 [110/20] via 172.16.1.1, 00:41:36, Serial0/0
- Kiểm tra việc quảng bá tuyến cho CustomerB
PE2-AS1#show ip route vrf CustomerB ospf 202
O E2 192.168.199.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.2.2, 00:44:06, Serial1/2
O E1 192.168.99.0/24 [110/801] via 192.168.2.2, 00:44:06, Serial1/2
O 192.168.20.0/24 [110/791] via 192.168.2.2, 00:44:06, Serial1/2
PE2-AS1#show ip bgp vpnv4 all | begin 192.168.20.0
*> 192.168.20.0 192.168.2.2 791 32768 ?
*> 192.168.99.0 192.168.2.2 801 32768 ?
*> 192.168.199.0 192.168.2.2 20 32768 ?
PE1-AS1#show ip bgp vpnv4 all | begin 192.168.20.0
*>i192.168.20.0 10.10.10.102 791 100 0 ?
*>i192.168.99.0 10.10.10.102 801 100 0 ?
*>i192.168.199.0 10.10.10.102 20 100 0 ?
CE1-B#show ip route ospf
O E2 192.168.199.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.1.1, 00:12:06, Serial0/0
192.168.201.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.201.1 [110/65] via 192.168.1.1, 00:35:15, Serial0/0
O E2 192.168.99.0/24 [110/801] via 192.168.1.1, 00:12:06, Serial0/0
O E2 192.168.20.0/24 [110/791] via 192.168.1.1, 00:12:06, Serial0/0
192.168.202.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.202.1 [110/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:12:06, Serial0/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.2.0 [110/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:12:06, Serial0/0
OSPF Sham-Link
Hình dưới mô tả mạng của ISP cung cấp các dịch vụ MPLS VPN cho các Customer A thuộc cùng VPN-A có sử dụng Backdoor Link.
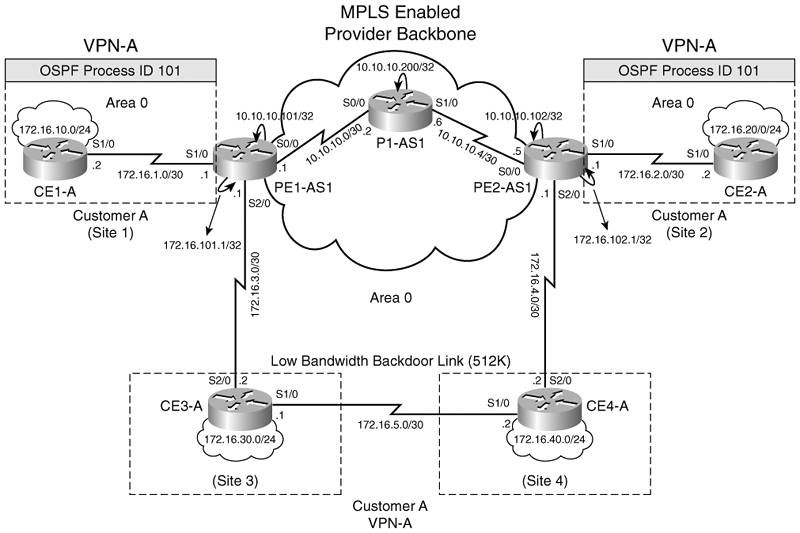
Customer A có 4 Site trong VPN-A. Các site đều thuộc Area 0. Site 3 và Site 4 được kết nối với nhau bằng một được backdoor link băng thông thấp (512 kbps). Backdoor link này cung cấp kết nối giữa Site 3 và Site 4 khi kết nối đến backbone của nhà cung cấp bị sự cố (down hoặc disconnected). Các site này cũng kết nối tới BGP-based MPLS VPN backbone của nhà cung cấp. Kiểu tích hợp này có thể xem là một dạng định tuyến kém tối ưu (suboptimal routing) như hình sau:
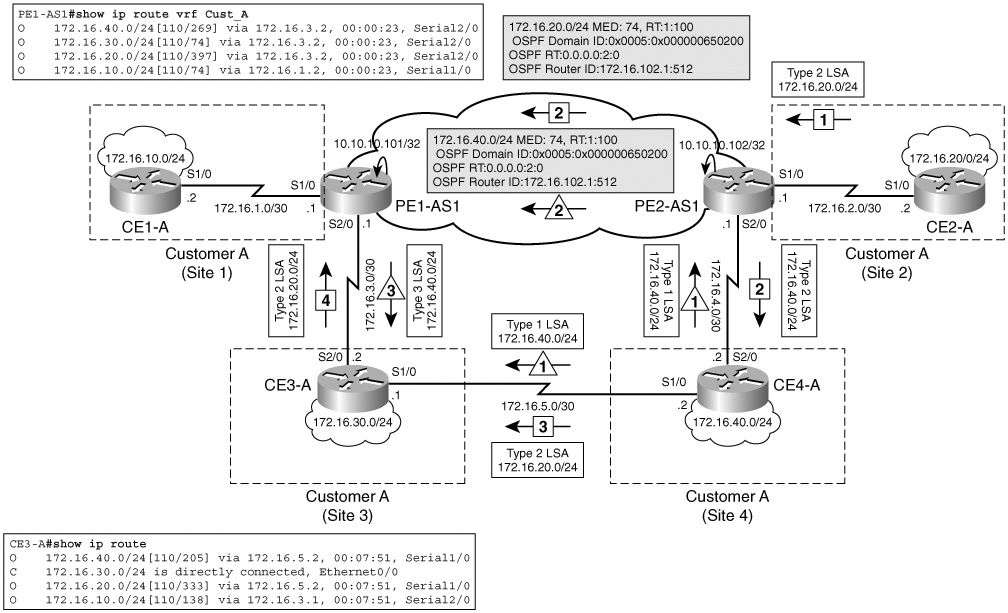
Trình tự thực hiện khi CE4-A quảng bá 172.16.40.0/24 tới cho CE3-A:
- CE4-A gửi một LSA Type 1 cho 172.16.40.0/24 tới PE2-AS1 và CE3-A.
- PE2-AS1 nhận 172.16.40.0/4 là một intra-area route, và redistribute vào MP-BGP.
- PE1-AS1 redistribute 172.16.40.0/24 vào OSPF và quảng bá 172.16.40.0/4 là một intra-area route tới CE3-A.
- CE3-A nhận được hai inter-area route 172.16.40.0/24 từ PE1-AS1 và một intra-area route từ CE4-A. Vì intra-area route được ưu tiên hơn nên được thêm vào cơ sở dữ liệu OSPF (OSPF database).
Trình tự này cùng xảy ra với 172.16.30.0/24 khi nó được CE2-A quảng bá đi. Do đó, các gói dữ liệu xuất phát từ 172.16.30.0 (Site 3) tới 172.16.40.0 (Site 4) sẽ qua backdoor link. Tương tự cho các luồng lưu lượng bắt nguồn từ 172.16.10.0 (Site 1) tới 172.16.20.0 (Site 2) vì bất kỳ tuyến liên quan nào từ MPLS VPN backbone sẽ là các inter-area route và intra-area route thì được ưu tiên hơn. Vì thế, việc chuyển tiếp lưu lượng dạng này được gọi là suboptimal vì backdoor link có băng thông thấp và được dùng để dự phòng (backup). Bên dưới cho thấy đường chuyển tiếp lưu lượng trong mạng MPLS VPN sử dụng backdoor link (không sham link).
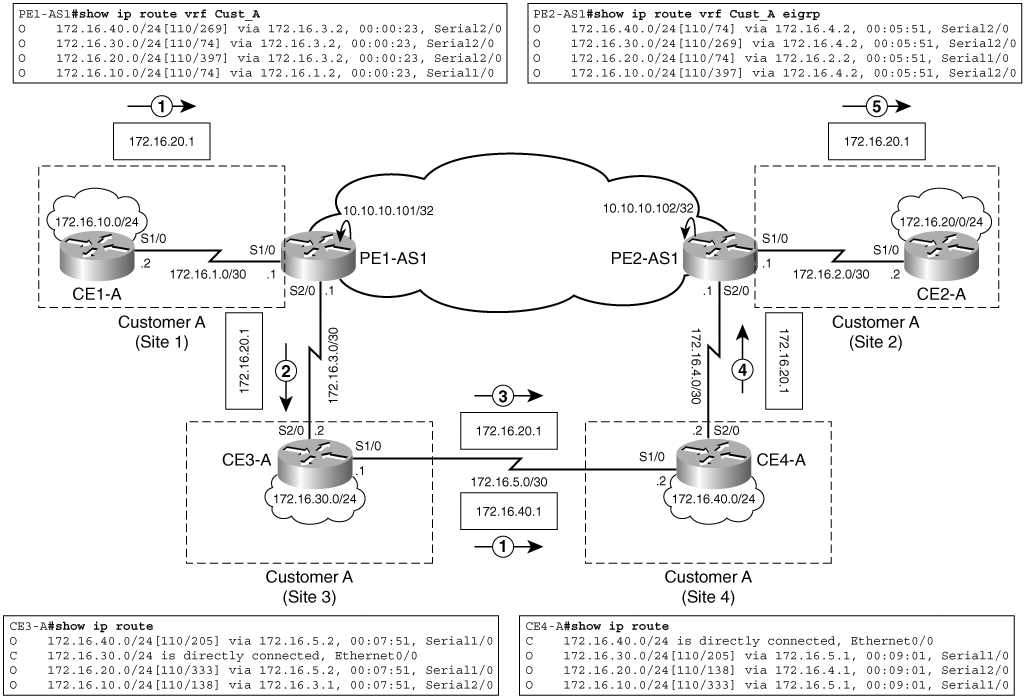
Có thể tránh trường hợp này bằng cách sử dụng một sham-link. Một sham-link là một kết nối luận lý (logical link) thuộc về nội vùng (intra-area) nhưng không được mang theo bởi BGP-based superbackbone. Hai router PE sẽ là endpoint của sham-link. Chúng sẽ thiết lập một OSPF adjacency đi qua và floot các intra-area LSA qua kết nối này. Sham-link được xem là một mạch ảo theo yêu cầu (DC – demand circuit) của OSPF nhằm giảm luồng lưu lượng qua sham-link. Điều này giúp tránh việc các LSA được floot định kỳ qua sham-link. Hình sau mô tả một sham-link:
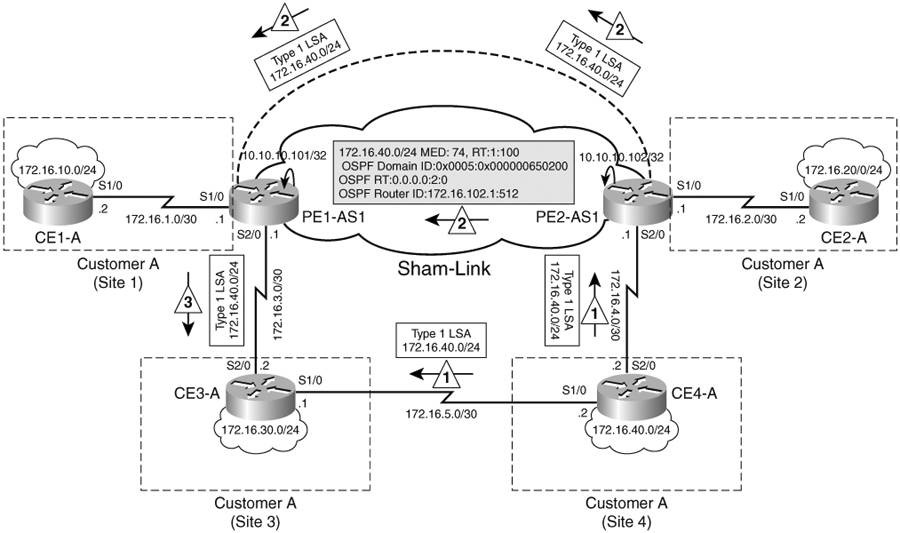
CE4-A gửi 172.16.40.0/24 vớ LSA Type 1 tới CE3-A, sau đó LSA này được quảng bá tới PE1-AS1. PE1-AS1 nhận được OSPF-LSA Type 1 từ CE4-A qua CE3-A và từ PE2-AS1 qua OSPF sham-link. OSPF sham-link được đối xử như một kết nối nội vùng (intra-area link) giữa PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1. Cost của sham-link có thể được cấu hình sao cho thấp hơn cost của backup link giữa CE3-A và CE4-A. Do đó PE2-AS1 redistribute tuyến 172.16.40.0/24 vào MP-BGP vì tuyến OSPF này không được nhận qua một sham-link từ PE1-AS1. PE1-AS1 cũng không redistribute tuyến này vào MP-iBGP vì nó không được nhận từ PE2-AS1 qua OSPF sham-link. PE1-AS1 cài đặt tuyến OSPF nhận được từ sham-link vào bảng định tuyến VRF của nó. LSA cho tuyến 172.16.40.0/24 được quảng bá đến Site 4 để cho phép Site 3 chọn đường đi tốt nhất. Khi đó, các gói nhận được từ Site 4 sẽ được định tuyến qua MPLS VPN backbone và sử dụng kết nối băng thông cao. Như vậy, CE3-A tại Site 3 cũng chọn sham-link là đường đi tốt nhất đến 172.16.40.0/24. Vì thế luồng lưu lượng giữa giữa Site 3 và Site 4 được định tuyến tối ưu qua sham-link giữa PE1-AS1 và PE2-AS1.
Sơ đồ cấu hình cho OSPF Sham-Link
